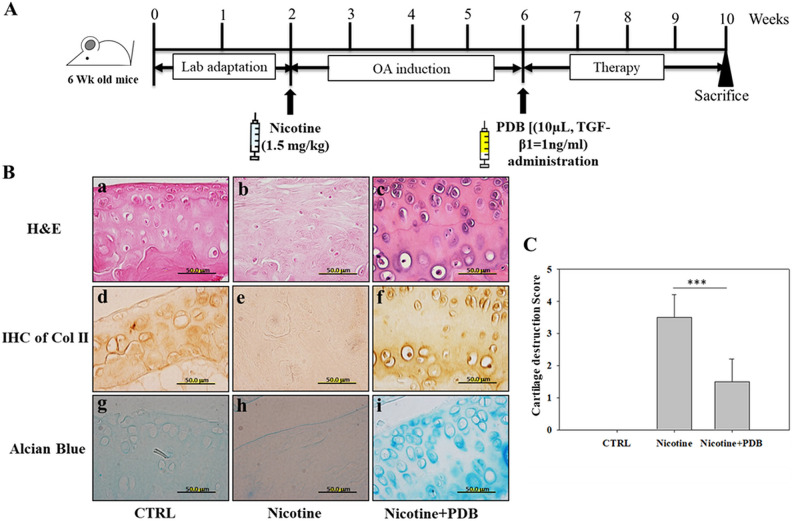
Figure 4.
PDB administration and assessment of OA-associated histologic improvements. (A) Experimental protocol for PDB therapy in nicotine-induced OA mice. Following 2 weeks of lab adaptation, mice knee joint (n = 5) was subcutaneously injected with nicotine (1.5 mg/kg) for 4 weeks. Thereafter, PDB was intra-articularly injected in the animals (n = 5) once per week for 4 weeks, and the improvement in OA status was examined after further 4 weeks of treatment time. (B) Representative H&E staining (a–c, upper panel), immunohistochemical staining of Col II (IHC Col II) (d–f, middle panel), and alcian blue staining (g–i, lower panel) were conducted to determine the ultrastructural changes, collagen and proteoglycan content, respectively, in the extracellular matrix of articular cartilage of control, nicotine-treated, and PDB-treated nicotine-OA group. All the images were obtained at ×100 magnification (scale bar: 50 µm). Further, based on these histologic analyses, the severity of OA score (C) was determined. The results are presented as mean ± SD [n = 3 (control); n = 5 (nicotine and nicotine + PDB); *** P < 0.001]. H&E: hematoxylin & eosin; OA: osteoarthritis; PDB: platelet-derived biomaterial; SD: standard deviation.