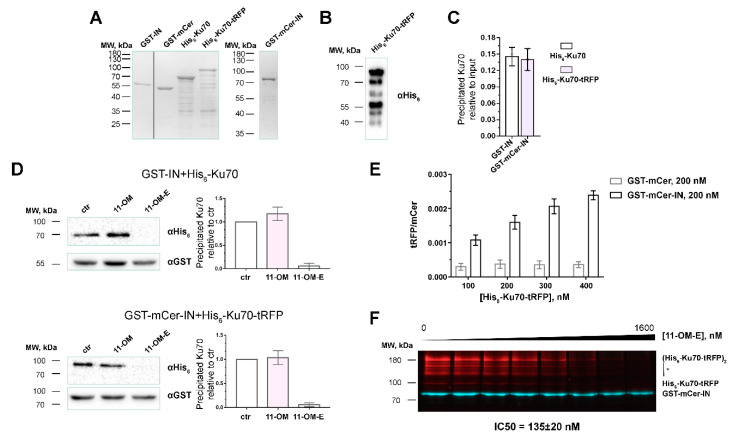
Figure 2.
Validation of the fluorescent assay for the discovery of Ku70-IN inhibitors. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant proteins GST-IN, GST-mCer, GST-mCer-IN, His6-Ku70, His6-Ku70-tRFP. (B) Western-blot analysis of His6-Ku70-tRFP purity using an anti-His6 antibody. (C) GST-mCer-IN (200 nM) binds His6-Ku70-tRFP (200 nM) at the same amount as GST-IN (200 nM) binds His6-Ku70 (200 nM). (D) Interaction of 200nM GST-IN and His6-Ku70 or GST-mCer-IN and His6-Ku70-tRFP in the absence or in the presence of well-characterized inhibitor 11-OM-E (1µM) or control compound 11-OM (1µM) is analyzed by GST-pull-down assay with subsequent WB analysis against GST and His6-tags. ctr–control, binding of proteins in absence of 11-OM-E or 11-OM. (E) Precipitation of His6-Ku70-tRFP with GST-mCer-IN or GST-mCer analyzed by the method described here in 96-well plate format. (F) Fluorescent pull-down assay analysis of the interaction of His6-Ku70-tRFP (200 nM) and GST-mCer-IN (200 nM) in the presence of an increasing concentration of 11-OM-E. * signed dimers of the full-length His6-Ku70-tRFP and N-terminal degraded forms.