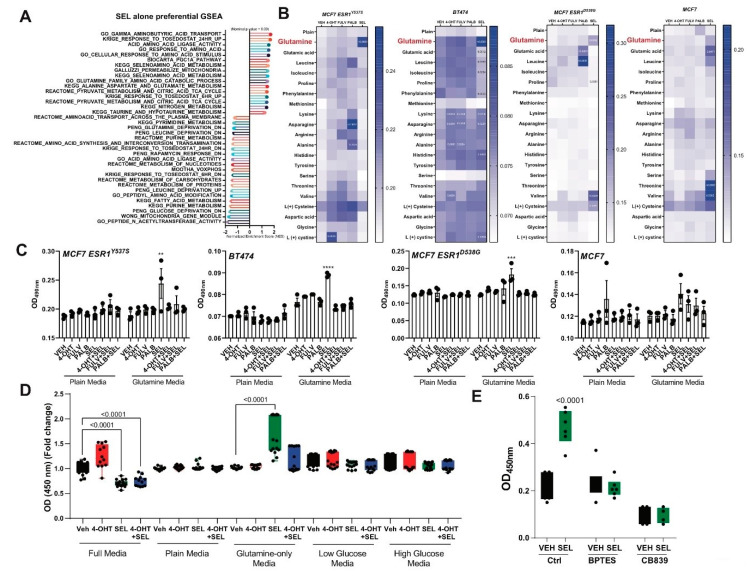
Figure 3.
(A) Single agent treatments and growth on metastatic organ sites rewire metabolic pathways to enhance survival of BCa cells A. GSEA analysis showing activation of amino acid deprivation genes in MCF7-ESR1Y537S cells. (B) Endocrine-sensitive MCF7 cells, endocrine-resistant MCF7-ESR1Y537S, MCF7-ESR1D538G or BT474 cells were grown in minimal media containing only 2 mM individual amino acids. Cells were treated with different endocrine agents (1 µM 4-OHT, Fulv or Palb, and 100 nM SEL) and cell viability was quantified with WST-1 assay. All experiment conditions were repeated in six technical replicates and statistical significance values were calculated according to two-way ANOVA test. (C) Endocrine-sensitive MCF7 cells, endocrine-resistant MCF7-ESR1Y537S, MCF7-ESR1D538G or BT474 cells were grown in minimal media conditions supplemented only 2 mM individual amino acids. Cells were treated with different endocrine agents (1 µM 4-OHT, Fulv or Palb, in the presence or absence of 100 nM SEL) and cell viability of cells were quantified with WST-1 assay. All experiment conditions were repeated in six technical replicates and statistical significance values were calculated according to two-way ANOVA test. ** p < 0.01, *** p <0.001, **** p < 0.0001. (D) Cell viability assay showing the effect of glutamine addition to the media. BT474 cells were cultured at a density of 2 × 103 cells/well in a 96-well plate and treated with 1 µM 4-OHT alone and in combination with 100 nM SEL in different limiting media conditions. (E) Similar experimental conditions were tested in presence of 1 µM Glutaminase inhibitors, BPTES or CB839. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) model was used for statistical significance of treatment and values were presented as mean ± SEM from three independent experimental repeats.