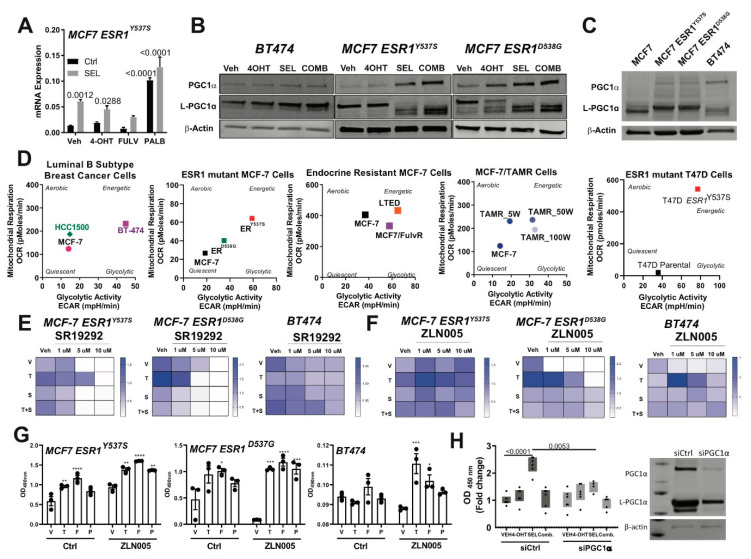
Figure 5.
PGC1α drives the metabolic rewiring in response to metastatic niche and therapies. (A) RNA sequencing results showing SEL treatment induces PPARGC1A (PGC1α) mRNA expression alone or in combination with other therapy agents. Statistical analyses were analyzed according to one-way ANOVA test. Western blot analyses showing that PGC1α protein expression was relatively higher in cells that were treated with SEL (B) or in endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells (C). All cell lines were seeded at a density of 2 × 105 cells/30 mm plates. Cell lysates were prepared and western blot analysis was performed. (D) Cellular metabolic phenotype changes in different endocrine-sensitive and -resistant models were monitored with Seahorse metabolic profiling. Different de novo endocrine-resistant cell models (HCC1500, BT474, MCF7-ESR1D538G and MCF7-ESR1Y537S) and acquired resistant models (TamR cells generated with a consistent drug treatment strategy) were cultured at a density of 3 × 104 cells/XFp plate wells, and treated with different endocrine agents (1 µM 4OHT, Fulv and Palb) and in combination with 100 nM SEL. The impact of PGC1α function on the cell viability of BT474 cells was tested. BT474 cells were seeded in 96-well plates, and treated with 1 µM 4-OHT alone and in combination with 100 nM SEL with a PGC1α inhibitor, SR19292 (E) or PGC1α activator, ZLN005 (F). A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) model was used for statistical significance of treatment and values were presented as mean ± SEM from three independent experimental repeats. Significances were compared according to first measurement values for each treatment condition. (G) The impact of PGC1α function on the cell viability of BT474 cells was tested. BT474 cells were seeded in 96-well plates, and treated with 1 µM 4OHT, Fulv or Palb alone and in combination with 100 nM SEL with ZLN005. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p <0.001, **** p < 0.0001. (H) Cell viability assay in the presence of glutamine only media with PGC1α knock-down in BT474 cells.