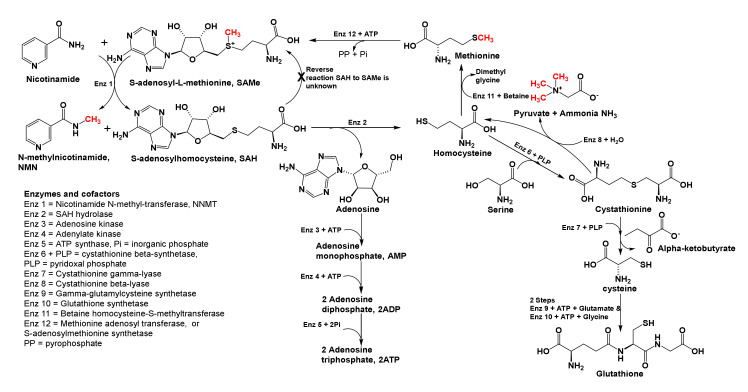
Figure 5.
Methyl transfer by SAMe, B12, or betaine; syntheses of ATP, cystathionine, cysteine and glutathione; and regeneration of SAMe. Methyl and other alkyl group transferases take the name of the substrate they methylate or alkylate; for example, nicotinamide-N-methyl transferase, NNMT methylates nicotinamide, as shown here. All methyl groups in transfer reactions herein are shown in bold red font. SAMe and NNMT convert nicotinamide to NMN and SAH. However, SAH does not directly revert to SAM; instead, SAH is hydrolyzed to adenosine and homocysteine. Either a molecule of SAMe, vitamin B12, or betaine can convert homocysteine to methionine, which then reforms SAMe. Upon formation, adenosine is eventually converted to ATP, and homocysteine to cystathionine that transulfurates with serine to form cysteine, and then glutathione [95,96,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109].