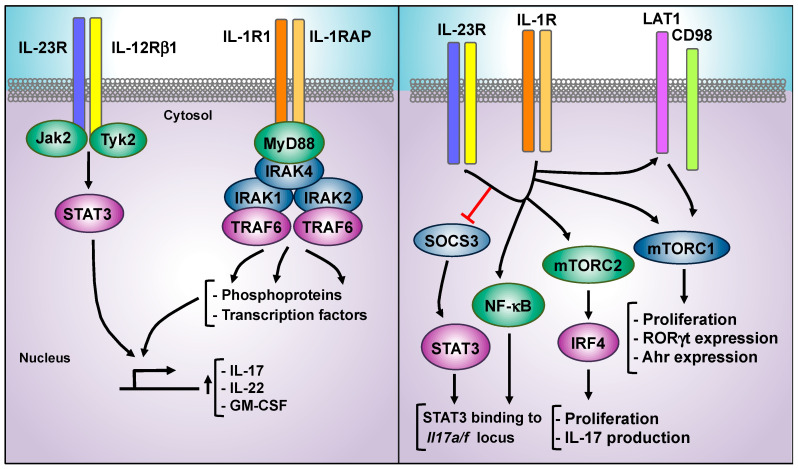
Figure 5.
IL-23 and IL-1β: signaling crosstalk. The combined action of IL-23 and IL-1β greatly increases the production of IL-17, IL-22, and GM-CSF. Right, IL-23 and IL-1β signaling cascades at a glance: IL-23 signaling cascade is mediated by the JAK/STAT module, while IL-1β signal is transduced by MyD88/IRAKs/TRAF6 module. MyD88/IRAKs/TRAF6 induce the activation of several phosphoproteins and transcription factors. Left, IL-1β stimulation decreases IL-23-induced expression of Socs3 in an NF-κB-dependent manner, and decreased Socs3 expression upon IL-23/IL-1β stimulation leads to an increased STAT3 phosphorylation. IL-1β-induced NF-κB/RelA activation increased the binding of IL-23-induced STAT3 to regulatory elements in the Il17a/f locus. IL-23 and IL-1β promote mTORC1 and mTORC2 activation. IL-23/IL-1β activation of mTORC2 induces the expression of the transcription factor IRF4, required for IL-17 production and Tγδ cell proliferation. IL-23/IL-1β-induced mTORC1 activation promotes Tγδ cell proliferation and induces RORγt and AhR expression in neutrophils. IL-23/IL-1β co-stimulation increases the expression of LAT1 and induces the activation of mTORC1 and the proliferation in Tγδ17 cells.