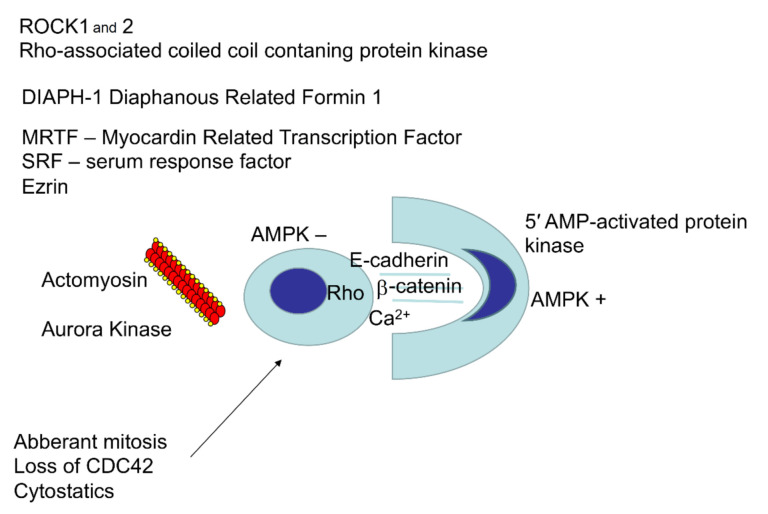
Figure 2.
The main known molecules regulating entosis. The central part represents a schematic view of the cell–cell interaction during entosis. On the left, the interior cell is rounded after losing its contact with the substrate. On the right, the outer cell wraps around the inner cell and has a crescent-shaped nucleus. Both cells interact through formation of adhesion junctions mediated by E-cadherin, β-catenin, and calcium ions. The protein kinase AMPK is active in the outer cell and inactive in the inner one. On the left, there is a list of molecules that are active in the inner cell. The arrow indicates factors inducing entosis in cancer cells.