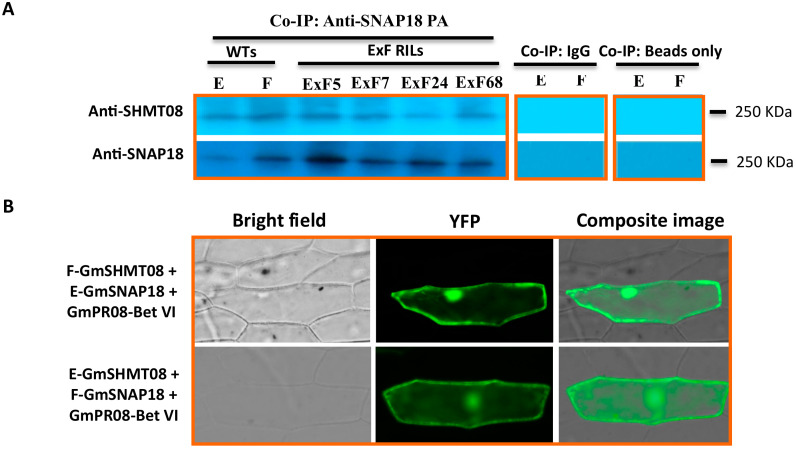
Figure 2.
Interaction analyses of GmSNAP18 and GmSHMT08 proteins carrying resistant and susceptible allele combinations by Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and BiFC assay. (A) The total protein extracts of soybean Forrest, Essex, and four ExF RIL (Figure S1) roots were immunoprecipitated with Anti-GmSNAP18 PA. Blots from the eluted fraction were probed with both anti-SHMT08 and Anti-GmSNAP18. Upper bands on the panel (~ 250 KDa) correspond to the multi-protein complex including the tetrameric GmSHMT08 protein, lower bands on the panel (~ 250 KDa) correspond to the multi-protein complex including the GmSNAP18 protein. Native PAGE conditions (non denaturant) and western hybridization of the eluted fraction using both anti-GmSHMT08 and anti-GmSNAP18 antibodies showed the co-localization of the GmSHMT08 and GmSNAP18 binding. IgG and beads were used for Co-IP experiments as a negative control and technical control, respectively (B) BiFC analysis between GmSHMT08, GmSNAP18, and GmPR08-Bet VI proteins. The coding sequences of resistant Forrest (F) and susceptible Essex (E) alleles from GmSNAP18 and GmSHMT08 were cloned into pSAT4-nEYFP-C1-B and pSAT4-cEYFP-C1 to generate nEYFP-SNAP18 and cEYFP-GmSHMT08 fusions, respectively. GmPR08-Bet VI was cloned into pG2RNAi2. Various combinations of cEYFP and nEYFP control fusions were co-expressed in onion epidermal cells by particle bombardment (Figure S2). Co-IP and BiFC assays indicated that resistant and susceptible alleles of GmSNAP18 and GmSHMT08 can associate each other.