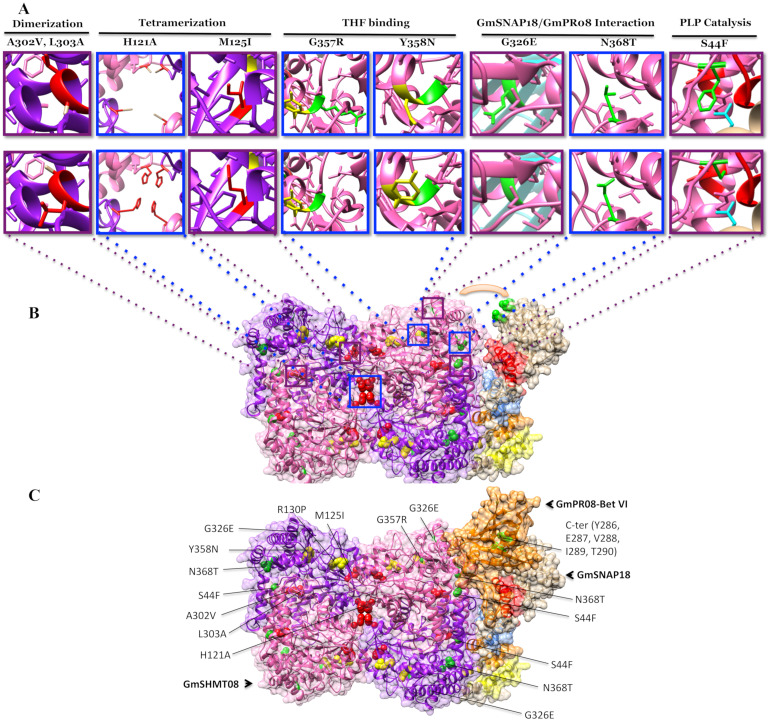
Figure 4.
Mutational analysis supports the GmSNAP18/GmSHMT08/GmP08-Bet VI multi-protein complex predicted model. (A) The nine Gmshmt08 mutant alleles used in the mutational analysis to study the predicted homology model (multi-protein). (down panel) represents the original residues in the Forrest WT, (up panel) represents the mutated residues (Induced and natural occurring mutations). (B) The predicted interaction between GmSHMT08 (left) and GmSNAP18 (Right). The surface in the middle (orange arc) correspond to the pocket where GmPR08-Bet VI protein was predicted to fit. Locations of the four TPR motifs (TPR1: Yellow, TPR2: Orange, TPR3: Blue, TPR4: Red) and polymorphisms (Green) at the GmSNAP18 are shown (Right). (C) The predicted interaction between GmSNAP18, GmSHMT08, and GmPR08-Bet VI protein complex. GmSHMT08 EMS induced mutations affecting Dimerization (red), Tetramerization (red), and Interaction (Green) with GmSNAP18 and GmPR08-Bet VI proteins are shown. The two polymorphisms R130P and Y358N between Essex and Forrest are shown in yellow. The GmSHMT08 EMS mutant M125I was identified earlier by TILLING (Liu et al., 2012); EMS mutants S44F, A302V, G326E, and N368T were identified by forward genetic (Kandoth et al., 2017). The EMS mutant G357R was identified by TILLING in this study. GmSHMT08Δ+H121A, GmSHMT08ΔM125I, GmSHMT08Δ+L303A, GmSNAP18Δ+E208D, GmSNAP18Δ+Y286D, GmSNAP18Δ+E287D, GmSNAP18Δ+V288*, and GmSNAP18Δ+I289L mutations were produced by direct site mutagenesis in the current study and further tested their impact on the GmSHMT08/GmSNAP18/GmPR08 multi-protein complex complex by BiFC. The predicted interaction model was supported by BiFC analysis.