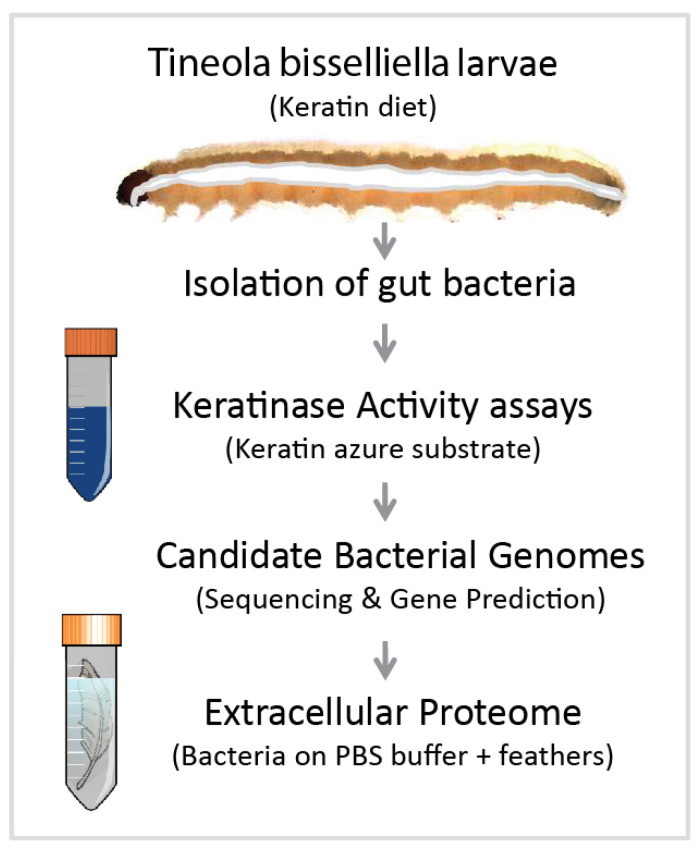
Figure 1.
Experimental workflow for the identification of keratin-degrading proteins in bacteria associated with the clothing moth Tineola bisselliella. Clothing moth larvae were reared on a keratin-based diet for several generations before the isolation of gut bacteria. Individual bacterial colonies were then tested for keratinase activity using keratin azure as a substrate. DNA was extracted from two bacterial isolates showing the strongest activity in the keratin azure assay as well as the ability to grow on whole feathers as a sole nutrient source. The genome sequence was screened for protein-coding genes allowing the identification of candidate keratinases. Extracellular proteins isolated from the supernatant of bacteria grown on feathers as a sole nutrient source were analyzed by LC MS-MS.