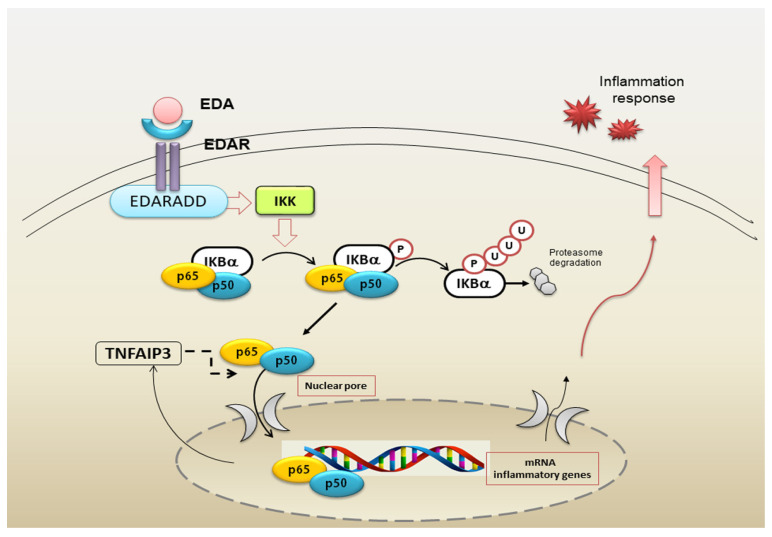
Figure 3.
Schematic overview of the EDA/EDAR/canonical NF-κB pathway. The EDA isoform of the TNF-α family member Ectodysplasin interacts with its receptor EDAR leading to the recruitment of EDARADD (death domain adaptor); in turn, this complex activates the IKK complex. The IKK complex phosphorylates IκBα, that undergoes ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation, inducing nuclear translocation of the NF-κB heterodimer RelA/p50 that triggers the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes, including those that encode the negative regulators IκBα and TNF-α-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3). EDA: Ectodysplasin-A; EDAR: Ectodysplasin-A Receptor; EDARADD: Ectodysplasin-A receptor-associated associated death domain.