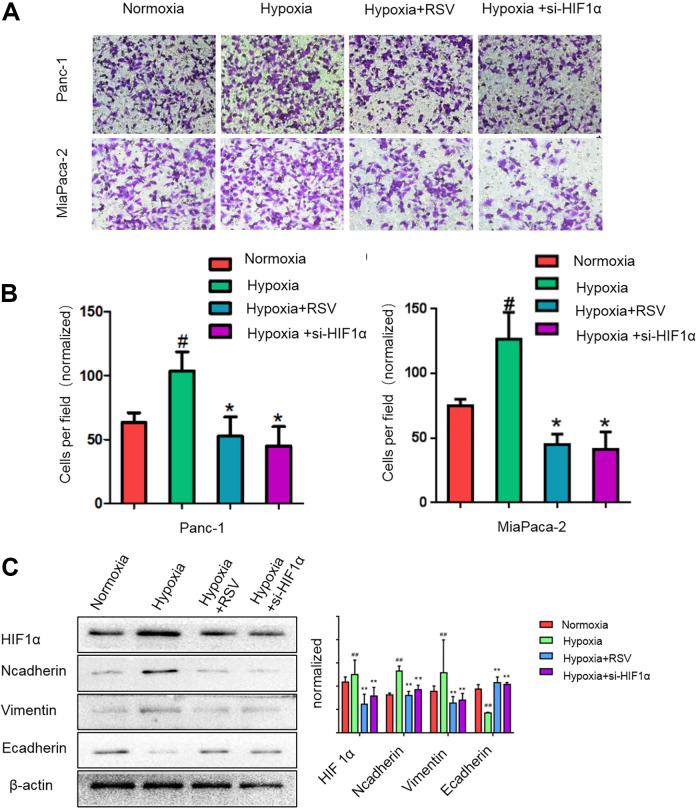
Fig. 2.
Resveratrol suppresses the pancreatic cancer cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition and invasion induced by hypoxia. (A, B) Panc-1 or Mia Paca-2 cells were incubated under normoxic conditions for 24 h or under hypoxic condition for 24 h in the presence of 50 μM resveratrol or si-HIF-1α. The cells were then seeded into a Matrigel-coated invasion chamber under normal or hypoxic conditions for 24 h. The invaded cells were quantified by counting the number of cells in 10 random fields at 200× magnification. (C) Subconfluent pancreatic cancer cells (Panc-1) were exposed to normoxia for 24 h or hypoxia for 24 h in the presence of 50 μM resveratrol or si-HIF-1α. HIF-1α, N-cadherin, vimentin, and E-cadherin expression levels in Panc-1 cells were analyzed by western blotting. #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01 comparing the hypoxia group with the control group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 comparing the hypoxia+RSV or hypoxia+si-HIF-1α group with the hypoxia group. All data represent at least three independent experiments. HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor 1; RSV: resveratrol.