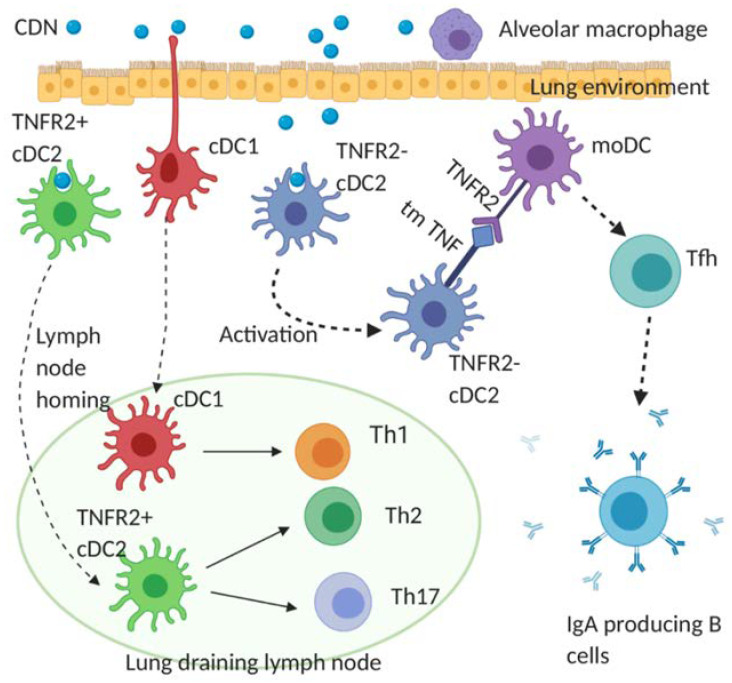
Figure 2.
Cellular mechanism of CDN adjuvanticity by lung DCs. Intranasal immunization of CDN promotes its uptake by functionally distinct lung DC subsets: cDC1, TNFR2+ cDC2, and TNFR2- cDC2. Upon the CDN uptake, cDC1 and TNFR2+ cDC2 mature and migrate towards the lung draining lymph node where they direct naïve T cells towards Th1, Th2, and Th17 effector cells. The TNFR2- cDC2 population, on the CDN uptake, is activated but does not migrate. Instead, the TNFR2- cDC2 produces transmembrane TNF, which engages TNFR2 on monocyte-derived DCs (moDCs) to trigger lung moDCs activation. Activated lung moDCs induce Tfh, GC formation, and IgA production in the lung.