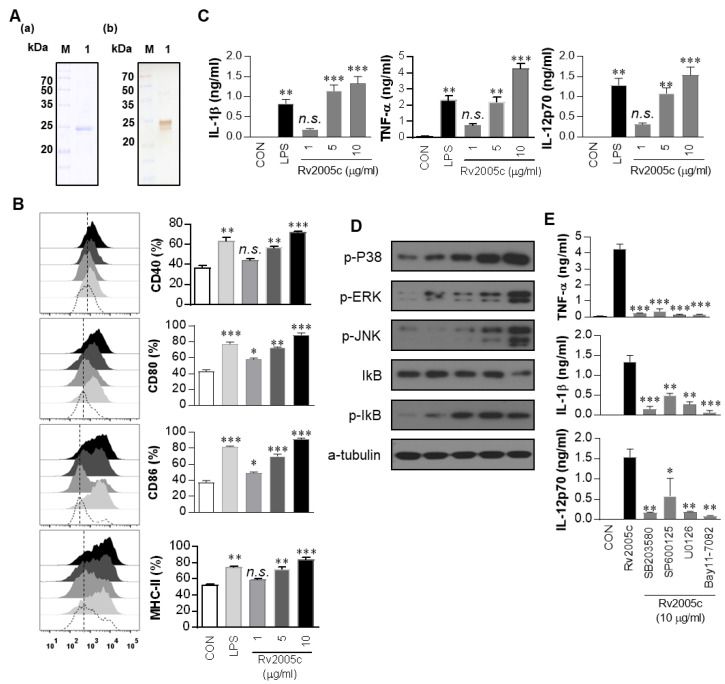
Figure 1.
Recombinant Rv2005c induces dendritic cell (DC) maturation through the MAPK pathway. (A) The purified, recombinant Rv2005c protein was subjected to (A) Coomassie blue staining sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and (B) western blot analysis using a mouse anti-His Ab. DCs were activated with the indicated concentration of Rv2005c or LPS (100 ng/mL) for 24 h. (B) Activated DCs were stained with anti-CD40, anti-CD80, anti-CD86, or anti-MHC class II Ab, and the expression of these surface markers was analyzed. The median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the positive cells is shown for each panel. The bar graphs show the mean ± SEM (n = 5). (C) The TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-12p70 levels in the culture medium were measured by ELISA. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 5). (D) The protein production by DCs treated with Rv2005c for the indicated periods was analyzed by immunoblotting using each specific Ab: phospho-p38 (p-p38), p38, phospho-ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2), phospho-IκB-α, and IκB-α. (E) DCs were pretreated with pharmacological inhibitors of p38 (SB203580, 20 μM), ERK1/2 (U0126, 10 μM), JNK (SP600125, 20 μM), Bay11-7082 (20 μM), or DMSO (vehicle control) for 1 h prior to treatment with 10 μg/mL Rv2005c protein for 24 h. The cytokine levels in the culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. The data shown are the mean ± SEM; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, or *** p < 0.001 for the inhibitor-treated samples compared to the Rv2005c-treated controls. n.s.: no significant difference.