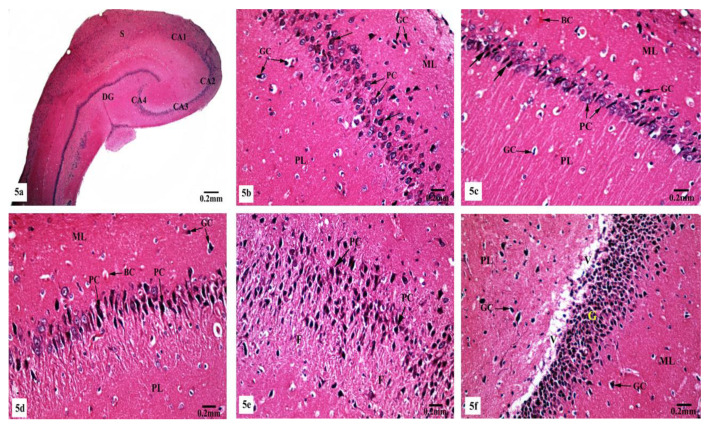
Figure 5.
Photomicrographs of the hippocampal tissues of AlCl3-treated rats stained with Hx&E showing (a) disruption of normal laminar organization, where the hippocampus appeared flattened, formed of CA1, CA2, CA3, and CA4 subfields, DG, and subiculum (S); (b) the CA1 subfield had disorganized small pyramidal cells (PC) and some of them appeared shrunken with pyknotic nuclei (→). Some glial cells (GC) appeared enlarged in the molecular (ML) and polymorphic (PL) layers; (c) another CA1 zone revealed marked shrunken small pyramidal cells (PC) and some of them showed pyknosis (→). Dilated congested blood capillaries (BC) and glial cells (GC) were also seen; (d) the CA3 subfield revealed large pyramidal cells (PC) exhibiting shrinkage with pyknotic nuclei, moreover, enlarged glial cells (GC) and dilated blood capillaries (BC) were noticed; (e) disorganized large pyramidal cells (PC) having pyknotic nuclei, in addition to fibrosis (F) were clearly seen in the surrounding neuropil in another CA3 area; (f) the granular cell layer (G) of the DG showed marked vacuolation (V). Molecular (ML) and polymorphic (PL) layers showed marked enlarged glial cells (GC).