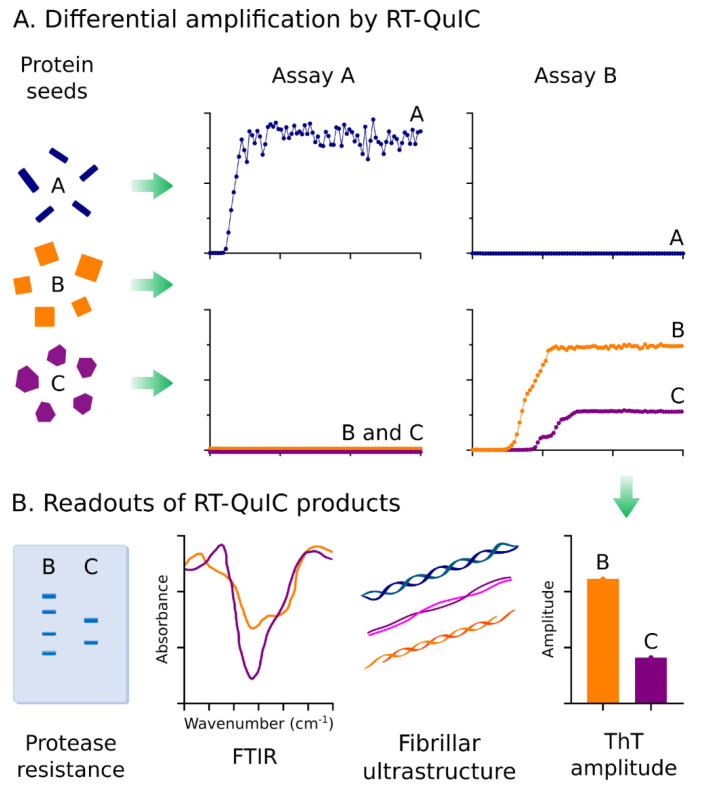
Figure 2.
Exploiting properties of protein seeds for differential diagnosis. (A) The conformational differences in protein seeds can be exploited for differential amplification using independent RT-QuIC assays that are selective for disease-specific protein seeds. Depicted is a theoretical representation of how two RT-QuIC assays (A&B) can be used to discriminate three different protein seed conformers. Seeds A can be discriminated from B & C using two selective assays capable of amplifying Protein Seed A (Assay A) or B & C (Assay B). Protein seeds B & C can be discriminated by ThT amplitudes within Assay B. (B) Conformational-based readouts of RT-QuIC fibrillar byproducts can be used to aid differential diagnosis of protein seeds via RT-QuIC. Fibrillar conformers amplified in RT-QuIC by distinct protein seeds can be reflected via differences in protease resistance, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy signatures (FTIR), fibrillar ultrastructures (e.g., visualized by electron microscopy), or ThT amplitudes.