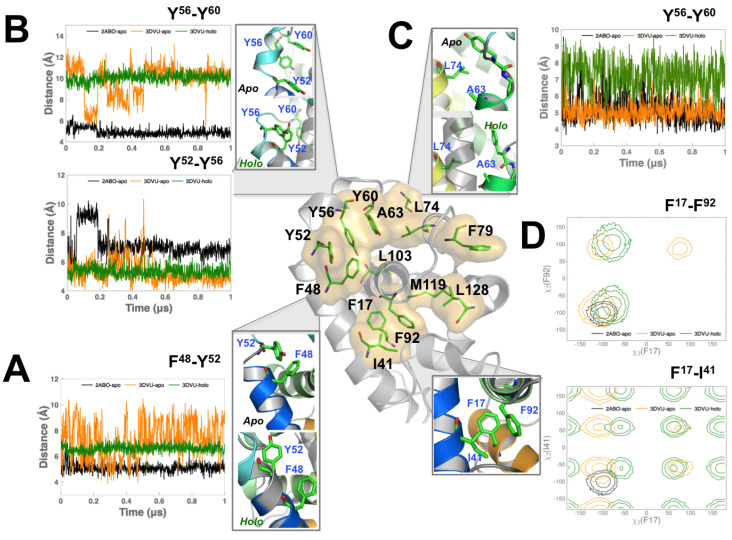
Figure 5.
Mutations to Viral BCL2 protein (vBCL2) residues far away from binding groove significantly impact binding of BECN1 BH3 domain. (A) Distance variation of Phe48 with Tyr52 in the 2ABO-apo (black), 3DVU-apo (orange), and 3DVU-holo (green) simulations. Note that the increase in the flexibility for Phe48 when BECN1 BH3D is removed from the binding site. (B) Distance fluctuations of the C atoms of Tyr52, Tyr56 and Tyr60 for the three simulations. While Tyr52-Tyr56 interaction in the 3DVU-apo simulation remains stable, a small segment of the simulation (from 0.2–0.4 s) indicates a partial unfolding in this region, sampling distances observed in the 2ABO-apo simulations. Tyr56-Tyr60 interaction on the other hand is stable in both the apo- and holo-M11 simulations, but undergoes dynamic fluctuations in the 3DVU-apo simulations. (C) Distance variation of Ala63 and its hydrophobic interactions with Leu74. Observe that upon binding BECN1 BH3D, the fluctuations in the distance between the C atoms of Ala63 and Leu74 increase when compared to the 2ABO-apo and 3DVU-apo simulations. (D) Hydrophobic interactions between Phe17, Phe92, and Ile41 quantified by the angle distributions of their respective side-chains. Up to three standard deviation intervals from the mean value of the values are depicted using respective color schemes that are described for the three simulations. For the Phe17-Ile41 side chain interaction, note that the 2ABO-apo simulations only sample a narrow range of angles; the 3DVU-holo and 3DVU-apo simulations sample additional states not seen in the 2ABO-apo simulations. For the Phe17-Phe92 interaction, there is overlap between the apo- and holo-M11 simulations, but the 3DVU-apo and 3DVU-holo simulations sample additional states not seen by the 2ABO-apo simulations.