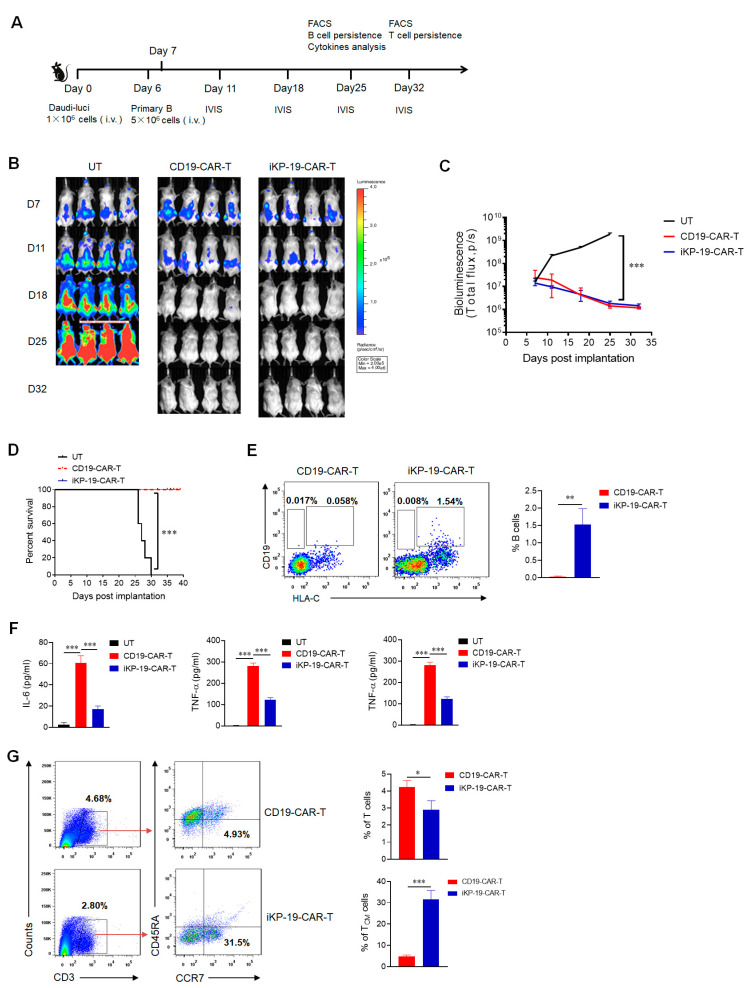
Figure 6.
Controlling B cell malignancy effectively with sparing normal B cells in vivo of iKP-19-CAR-T cells. (A) Schematic representation of in-vivo experimental design. NCG mice (n = 4/group) were i.v. injected with 1 × 106 luciferase-expressed Daudi cells (Daudi-luc) on day 0. After 6 days, 5 × 106 normal B cells were administered. At day 7, 5 × 106 UT cells, CD19-CAR-T cells and iKP-19-CAR-T cells were i.v. injected. IVIS imaging was performed to monitor tumor burden at day 11, 18, 25, 32. At day 25, normal B cells and cytokines in PB were analyzed. At day 32, T cells persistence was evaluated. (B) Representative bioluminescence images of Daudi-luc cells-derived tumor growth in the xenograft model. (C) Bioluminescence kinetics of Daudi-luc cells-derived tumor growth in the xenograft model. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of mice. (E) Representative presence of Daui cells (CD19+HLA-C1−) or normal B cells (CD19+HLA-C1+) in mice at day 25 was determined by flow cytometry using APC-anti-human CD19 antibody and PE-anti-human HLA-C antibody. (F) Cytokine secretion of IL-6, IFN-γ and TNF-α in PB at day25 was measured by using CBA assay kit. (G) Flow cytometer analysis of total numbers of T cells and central memory T cells (TCM) in different group of xenograft mice. T cells (CD3+) or TCM (CCR7+CD45RA−) were detected from PB by using APC-anti CD3 antibody, FITC-anti-human CD45RA antibody and PE/Cy7-anti-human CCR7 antibody. All the experiments were performed with 4 mice per group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001. Error bars represent ± SD.