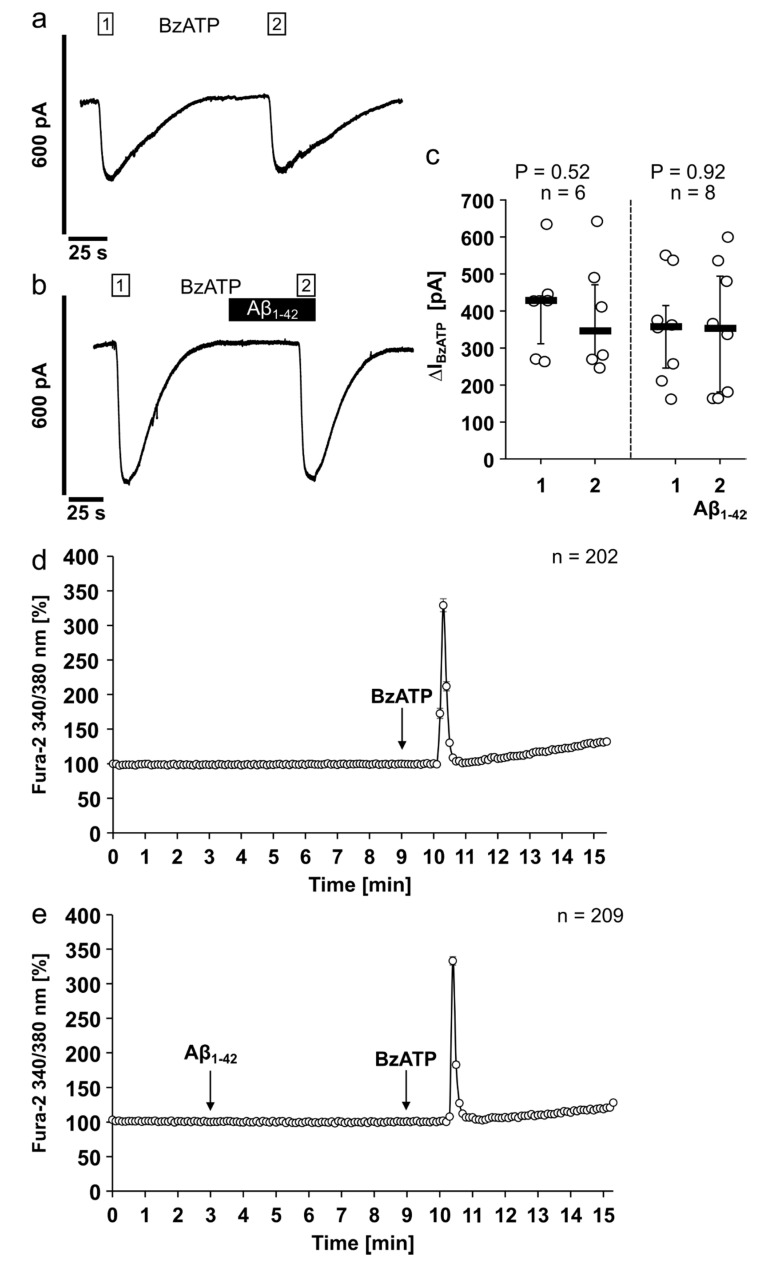
Figure 4.
Amyloid beta peptide (Aβ1-42) has no impact on the ion channel activity of the human P2X7 receptor. (a–c) Whole-cell patch-clamp measurements were performed on HEK293 cells overexpressing human P2X7 receptor (HEK-P2X7R cells). (a,b) Depicted are representative current traces. (a,c) In control experiments, consecutive application of the P2X7 receptor agonist BzATP (100 µM, white bar) induced repetitive current stimulations (BzATP1 and 2). (b,c) After washout of the first BzATP stimulus, Aβ1-42 (5 µM, black bar) was applied and did not induce changes in ion currents. In the presence of Aβ1-42, BzATP induced repetitive current stimulations. (c) All BzATP-induced current changes (∆IBzATP) are shown as individual data points, bar represents median, whiskers encompass the 25th to 75th percentile. Statistical analyses were performed using the Friedman test followed by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. (d,e) Calcium imaging experiments were performed on HEK-P2X7R cells. Intracellular calcium concentrations ([Ca2+]i) of HEK-P2X7R cells were recorded as Fura-2/AM (Fura-2) fluorescence intensity ratio of 340:380 nm excitation. For graphical representation and statistical analyses, signal intensities at time point 3 min were set to 100%, and all other values were calculated in accordance and are presented as mean ± SEM. (a) In control experiments, application of the P2X7 receptor agonist BzATP (100 µM) induced a rise in [Ca2+]i. (b) Aβ1-42 (5 µM) did not alter the [Ca2+]i. In the presence of Aβ1-42 additional application of BzATP induced a rise in [Ca2+]i. The BzATP-induced [Ca2+]i changes (∆[Ca2+]i) in the absence ((a); ∆[Ca2+]i = 239 ± 9%) and presence ((b); ∆[Ca2+]i = 233 ± 6%) of Aβ1-42 were not significantly different (p = 0.92; Mann–Whitney U test).