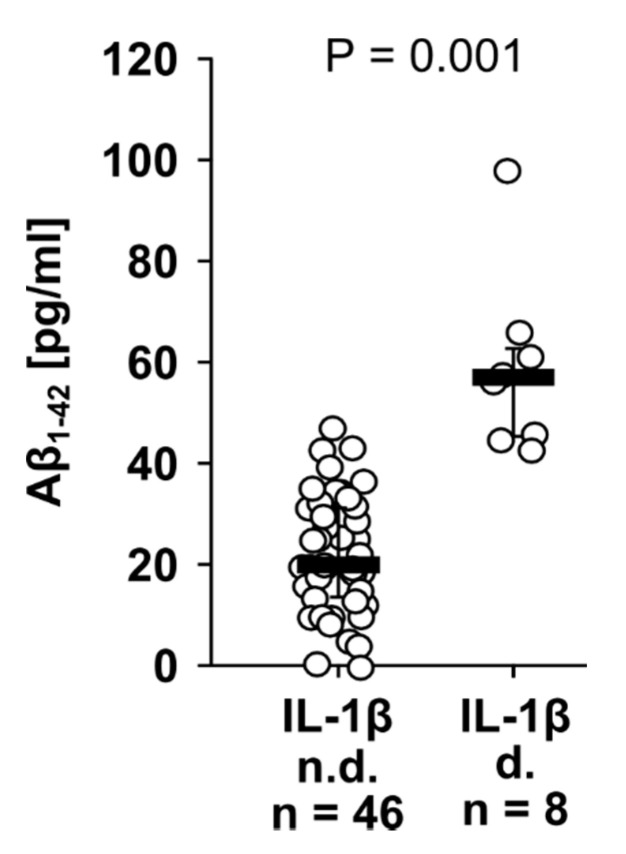
Figure 5.
Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) is predominantly detected in the blood of surgical patients together with increased amyloid beta (Aβ1-42) levels. Blood was drawn from patients, who underwent major surgery, shortly before the operation (n = 12), 0 to 2 h (n = 10), 24 to 48 h (n = 12), 72 to 96 h (n = 12), and 7 to 9 days (n = 8) after the operation. Aβ1-42 and IL-1β were measured by ELISA in patient blood plasma. Aβ1-42 values of patients, in whom IL-1β levels were below the threshold of detection (n.d.), were compared to patients with detectable IL-1β (d). Data obtained for all time points were investigated collectively and are shown as individual data points, bar represents median, whiskers encompass the 25th to 75th percentile. Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann–Whitney U test.