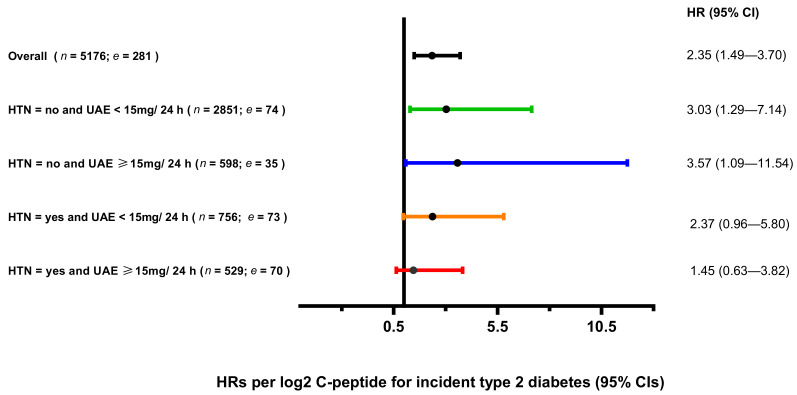
Figure 2.
Association between C-peptide and risk of type 2 diabetes in four subgroups. Multivariable hazard ratios (95% confidence intervals) for risk of diabetes are expressed per Log2-unit increase of C-peptide levels (n = number of subjects; e = number of events). Hazard ratios (95 CIs) were derived from Cox proportional hazards regression models with adjusted for age, sex, smoking status, alcohol consumption, BMI, family history of diabetes, triglycerides, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, eGFR, urinary albumin excretion, glucose, and insulin. HTN: hypertension; UAE: urinary albumin excretion; BMI: body mass index; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate.