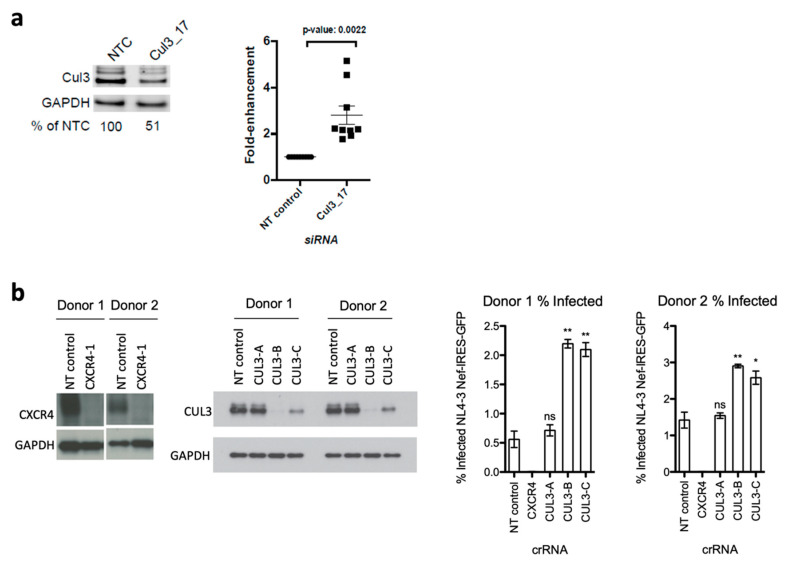
Figure 3.
Cul3 siRNA knock down and CRISPR/Cas9 knockout in primary CD4+ T cells increase HIV-1 infection. (a) Primary CD4+ T cells were isolated from nine independent blood donors and transfected with an Accell Cul3-targeting siRNA (Cul3_17) or a non-targeting control siRNA (NT control). 48 h post transfection, cells were infected by spinoculation with a VSVg-HIV-1 NL4-3 luciferase reporter virus. 48 h post infection, luciferase activity and cell viability were quantified using BrightGlo and CellTiter-Glo, respectively. Data is plotted as fold-change compared to NT control (n = 9). A representative Western blot from one donor is shown. (b) Primary CD4+ T cells, isolated from two independent blood donors, were electroporated with Cas9/gRNA ribonucleoprotein complexes (Cas9-RNPs) that target either Cul3 (three different guide RNAs: CUL3-A-C), CXCR4 or a non-targeting control (NT control). After nucleofection, cells were expanded for additional six days and, during that time, split every two to three days. Six days post electroporation, cells were either harvested to analyze knockout efficiency by western blot or infected with concentrated HIV-1 NL4-3 GFP reporter virus. 72 h post infection, percent infection was quantified based on GFP expression using flow cytometry. Data is plotted as mean of three technical replicates +/− SD. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.