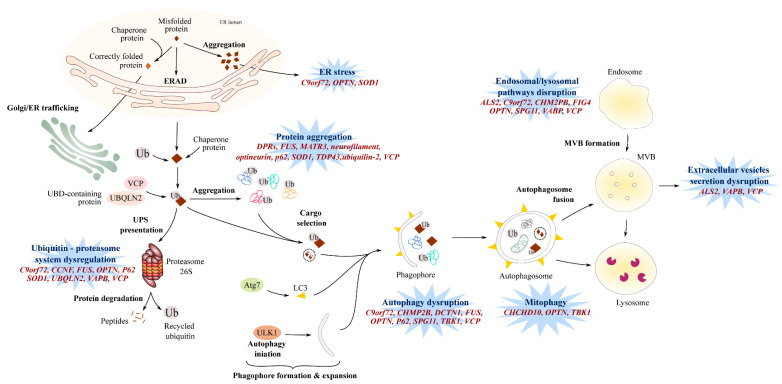
Figure 2.
Protein homeostasis dysregulation. Dysregulated protein homeostasis is mediated by multiple pathways encompassing defects in autophagy, the dysregulated ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), endo-lysosomal pathway disruptions, or endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. The presence of misfolded proteins activates endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation (ERAD), leading to proteasome-mediated degradation to avoid misfolded protein accumulations in the ER lumen and subsequent ER stress. Several ALS-associated gene mutations induce proteasome-mediated toxicity via the sequestration of ubiquilin and chaperone proteins involved in the UPS pathway. The proteolytic activity of the proteasome has also been demonstrated to be targeted by gene mutations in ALS. The autophagic pathway involves the formation and maturation of phagophores that engulf selected transported-cargo and form autophagosomes. Fusion with the lysosome enables the degradation of autophagosome contents. Defects in autophagy initiation and expansion, dysregulated phagophore formation, and/or impaired cargo transport are observed in ALS patients. Mutations in ALS-associated genes also cause defects in mitophagy, a specific form of autophagy. Defects in the endolysosomal have been associated with ALS gene mutations, including defective endolysosomal trafficking and altered lysosomal hoemostasis and degradation. Defects in the autophagy/lysosomal pathway may affect vesicle secretion. Genes implicated in dysregulated protein homeostasis are indicated in red. ER: endoplasmic reticulum, ERAD: endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation, ALS2: Alsin, C9orf72: Chromosome 9 open reading frame 72, CCNF: Cyclin F, CHCHD10: coiled-coil helix coiled-coil helix domain-containing 10, CHMP2B: chromatin-modifying protein 2B, DCTN1: Dynactin 1, FIG4: Phosphoinositide 5-phosphatase, FUS: Fused in Sarcoma, MATR3: matrin 3, MVB: Multivesicular bodies, OPTN: Optineurin, SOD1: Superoxide dismutase 1, SPG11: Spatacsin, TDP-43: TAR DNA-binding protein 43, TBK1: TANK-binding kinase-1, UBQLN2: Ubiquilin-2, VAPB: vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B, and VCP: valosin-containing protein.