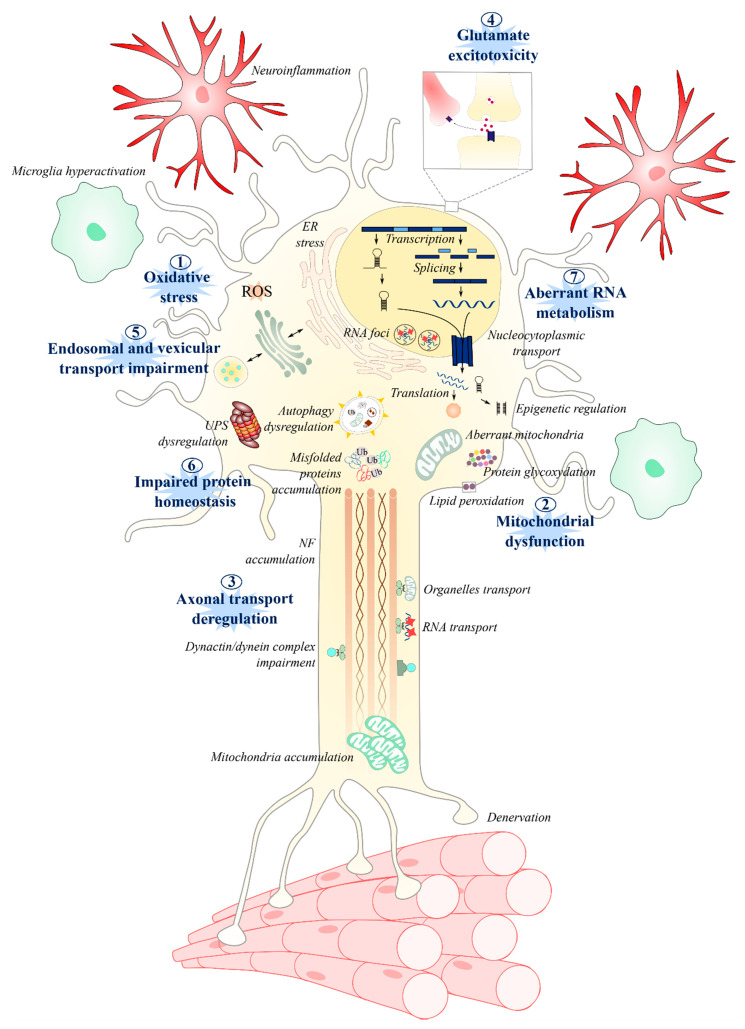
Figure 4.
Summary of the different molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in ALS pathogenesis. Among the most studied and well-established pathways are: oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, axonal transport, glutamate excitotoxicity, endosomal and vesicle secretions, protein homeostasis, and RNA metabolism. One pathway may lead to another, exacerbating the disruption of cellular homeostasis. The disruption of these pathways can lead to microglia activation, neuroinflamation, astrocytosis, and, ultimately, to motor neuron death and muscle denervation.