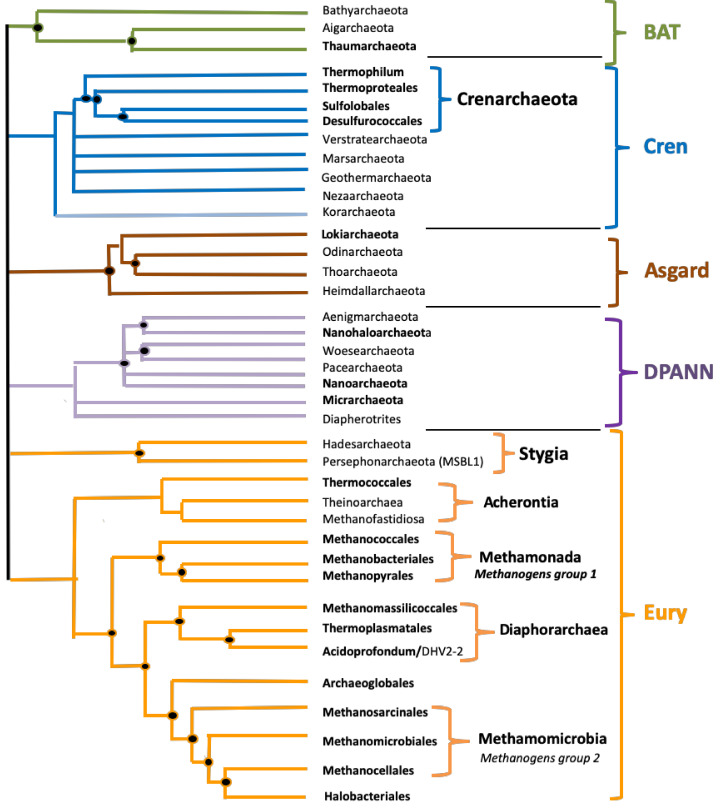
Figure 1.
A schematic phylogenic tree for Archaea. This unrooted evolutionary tree of Archaea is based on the schematic tree of Forterre (2015) [17] updated according to recent phylogenetic analyses [9,18]. BAT stands for Bathyarchaeota, Aigarchaeota, and Thaumarchaeota. DPANN is an acronym based on the first five groups discovered: Diapherotrites, Parvarchaeota, Aenigmarchaeota, Nanoarchaeota, and Nanohaloarchaeota. The term BAT superphylum has been proposed by Gaia et al. in 2018 [19], and the terms Eury and Cren superphyla are suggested here. The terms Cren superphylum is suggested here because the phyla Crenarchaeota, Verstratearchaeota Marsarchaeota, Nezaarchaeota, and Geothermarchaeota form a consensus monophyletic clade in all archaeal phylogeny. We included Korarchaeota in this superphylum because they often branch as sister groups of the above phyla in archaeal phylogenies, although the fast evolutionary rate made their positioning sometimes difficult. We suggested in parallel the term Eury superphylum because Euryarchaeota includes very diverse groups of cultivated and uncultivated Archaea which are difficult to the group in a single phylum, especially considering that phyla, such as Verstratearchaeota Marsarchaeota, or Nezaarchaeota only contain few uncultivated species only defined by a few metagenome associated genomes (MAGs). Names in bold letters correspond to subgroups that include cultivated species; names in thin letters correspond to subgroups that include only MAGs.