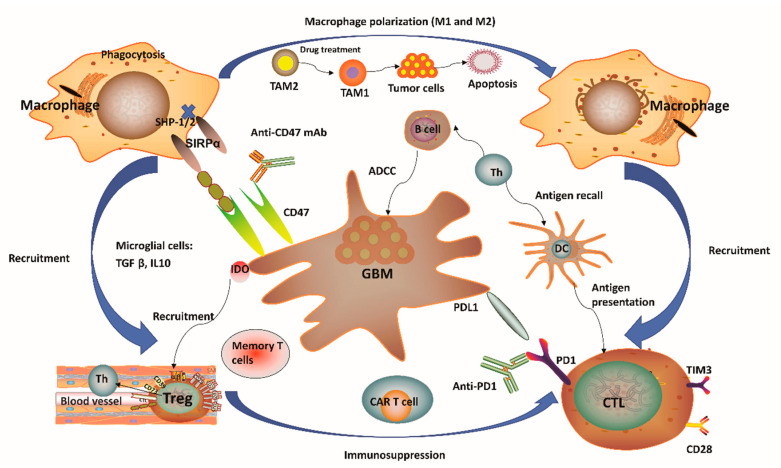
Figure 1.
Immunity-related microenvironment of glioblastoma. (1) The immune microenvironment involving glioblastoma (GBM) is characterized by large amounts of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, M1 and M2 polarized macrophages, microglia, and regulatory T (Treg) cells in addition to a limited number of natural killer (NK) cells. Tumor-associated macrophages and microglia (TAMs) have considerable plasticity toward anti-tumor M1 (inflammatory TAMs) and pro-tumor M2 (anti-inflammatory TAMs) phenotypes. Pharmacological strategies to re-educate tumorigenic M2 TAMs to tumoricidal M1 TAMs may help to relieve immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment (TME), as well as enhance the related anti-tumor activity. (2) GBM normally expressed high levels of immunosuppressive factors, such as programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) and indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), while limiting the presentation of antigens by decreasing major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presentation. The application of IDO inhibitors has effects on Treg cell accumulation. (3) CD47 is highly expressed in various types of tumors. Signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) is an inhibitory receptor expressed on macrophages and other myeloid immune cells. Upon CD47 binding to SIRPα, src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 (SHP-1) and SHP-2 phosphatases are activated to further abrogate phagocytosis via downstream mediators. Disruption of the CD47/SIRPα axis using anti-CD47 antibody (CD47 Ab) can interrupt the inhibitory signaling mediated by SIRPα, thereby promoting phagocytosis of tumor cells. (4) T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein-3 (TIM3) is a strong negative regulator of lymphocyte function and survival, acting as a marker of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell exhaustion similarly to programmed cell death 1 (PD-1). It has been verified that the co-expression of PD-1 and TIM3 in lymphocytes is positively correlated with the tumor grade, but it is negatively correlated with progression-free survival (PFS) in different types of tumors including GBM. (5) In the context of microglial cells, these often secrete transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) and/or interleukin 10 (IL-10) to decrease the amount of myeloid and/or lymphoid immune cells, resulting in a systemic immunosuppression and immune evasion of GBM cells. Th, helper T cell; ADCC, antibody-dependent-cell-mediated cytotoxicity; Treg, regulatory T cell; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; CAR T, chimeric antigen receptor T cell; DC, dendritic cell.