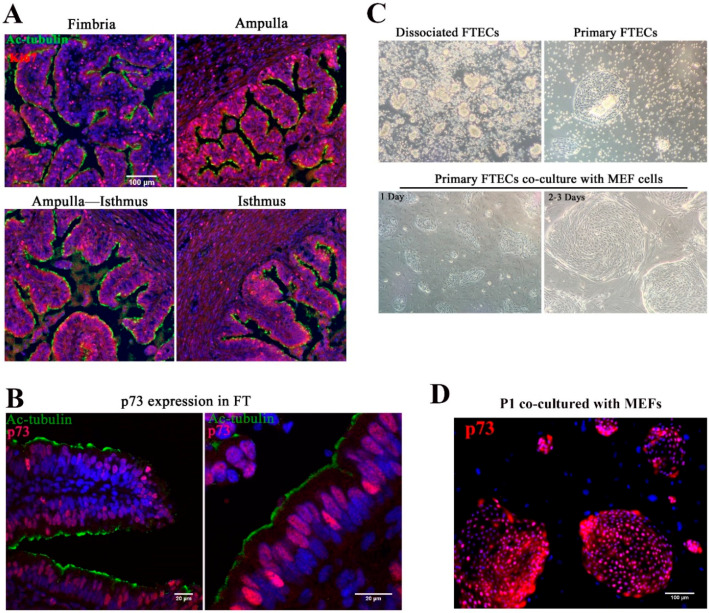
Figure 1.
Isolation and characterization of primary fallopian tube epithelium cells (FTECs). (A) Immunostaining of porcine fallopian tube epithelium from fimbria to isthmus by anti-acetylated-tubulin (Ac-tubulin) and anti-Ki67 antibodies, counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars: 100 µm. (B) Immunostaining of porcine fallopian tube epithelium by anti-acetylated-tubulin, -p73, and DAPI. p73 was used as basal cell marker for FTECs. Scale bars: 20 µm. (C) FTECs released from the FT after digestion with collagenase type IV and DNase I. Mobile small clumps that exhibited cilia were observed in the medium. These clumps were the source of primary FTECs. The cell clumps attached to the dish after 2 days in the presence of 10% FBS. After reaching confluence, the FTECs were trypsinized and co-cultured with proliferation-incompetent feeder mouse embryo fibroblast (MEF) cells in serum-free expansion medium. The FTECs grew in a colony-like manner, which became bigger during culture and reached confluence in 1 week. (D) Primary FTECs co-cultured with MEF cells in basal medium also showed p73-positive colonies. Scale bar: 100 µm.