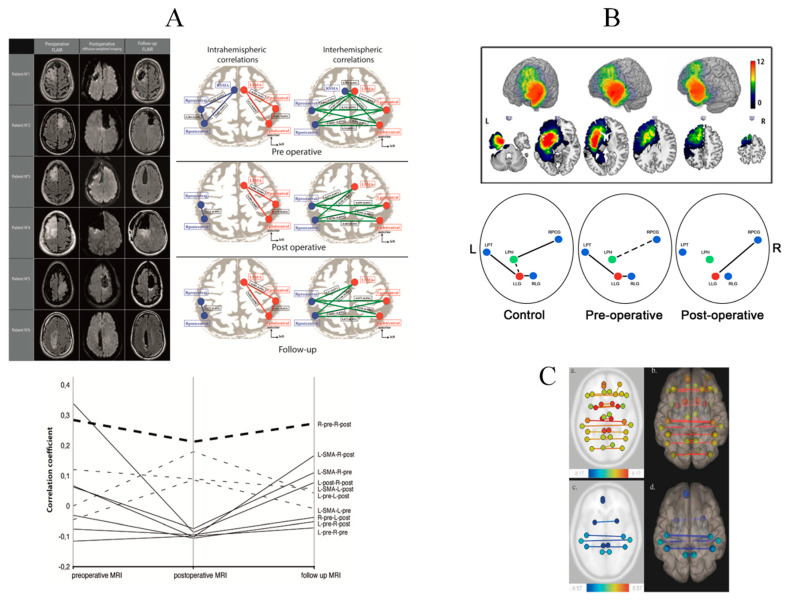
Figure 1.
Serial fMRI before and after LGG resection (A): perioperative motor reorganization (from [106]). Left: Preoperative FLAIR-weighted MRI (left column), immediate postoperative diffusion-weighted MRI (center column) and delayed postoperative FLAIR-weighted MRI in 6 patients who underwent resection for an LGG involving the SMA. Right: Evolution of correlation maps within the resting-state sensorimotor network. Correlation coefficients between the sensorimotor network nodes, at both intra-hemispheric (left column) and inter-hemispheric (right column) levels, in the preoperative period (top), in the immediate postoperative period (center), and at 3 months’ follow-up (bottom). In both hemispheres, network nodes include the precentral region, the postcentral region, and the SMA; the SMA was resected on the lesional side and is therefore absent postoperatively. Lower: Longitudinal evolution plot of inter- and intra-hemispheric correlations in the sensorimotor network. The time course of all intra-hemispheric (dashed lines) and inter-hemispheric (continuous lines) correlation coefficients within the sensorimotor network are presented, showing a temporary decrease. (B): perioperative language reorganization (from [107]). Upper: Tumor locations in 32 patients who underwent awake DEM surgery for a left LGG. The sum of all tumor masks in pre-operative condition is displayed. The value in each voxel corresponds to the number of tumors in this specific location (range (0–12)). Lower: Schematic description of the main FC results. The three conditions are displayed: control subjects and patients in pre-and post-operative conditions. Green and red dots correspond respectively to LPH and LLG. Solid lines highlight evidence of FC. Dashed lines show slight FC close to significance or identified using one to one comparison. The FC of the LLG in pre-operative condition is similar to the one in control subjects. The LPH is connected to RPCG in controls and still slightly connected pre-operatively. In the post-operative condition, LPH loses all FC while LLG modifies its connectivity to connect to RPCG as LPH in controls. Abbreviations: RPCG = Right Precentral Gyrus; RLG = Right Lingual Gyrus; LPT = Left Planum Temporale; LPH = Left Parahippocampal gyrus; LLG = Left Lingual Gyrus. (C). (from [108]) FC variations in 82 patients who underwent awake DEM surgery for an LGG. Patients were scanned using rsfMRI successively before surgery (MRI-1), immediately after surgery, within 36 h following surgery (MRI-2), and three months after surgery (MRI-3). Comparison of MRI-1 and MRI-2 (a, axial section) (b, 3-D superior view) show a functional homotopy decrease (yellow to red lines). Comparison of MRI-2 and MRI-3 (c, axial section) (d, 3-D superior view) show a functional homotopy increase (blue lines).