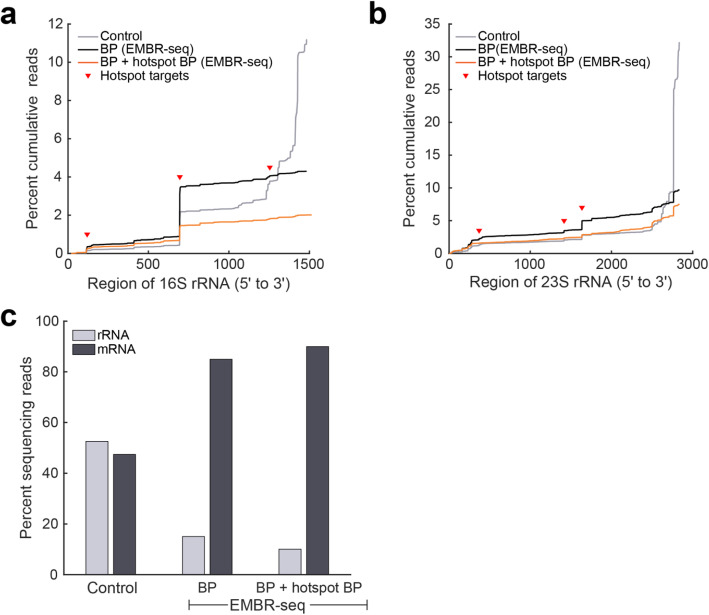
Fig. 4.
Additional hotspot blocking primers increase the rRNA depletion efficiency of EMBR-seq. a, b Cumulative percentage of sequencing reads ordered by mapping location along the (a) 16S and (b) 23S rRNA subunits, from 5′ to 3′ ends of the transcript. In the control group, the majority of mapped reads are derived from the 3′ end together with a few “hotspot” locations (red triangles) along the gene body (gray lines). In EMBR-seq, 3′ end blocking primers sharply reduce the number of reads derived from the 3′ end (black lines) with the remaining rRNA reads primarily deriving from hotspot locations. Additional blocking primers were designed to minimize poly-A tailing and amplification from the vicinity of these coordinates, resulting in further rRNA depletion (orange lines). c rRNA depletion and mRNA enrichment is enhanced upon the addition of hotspot blocking primers. With 3′ end and hotspot blocking primers in EMBR-seq, mRNA molecules account for 90% of the mapped reads