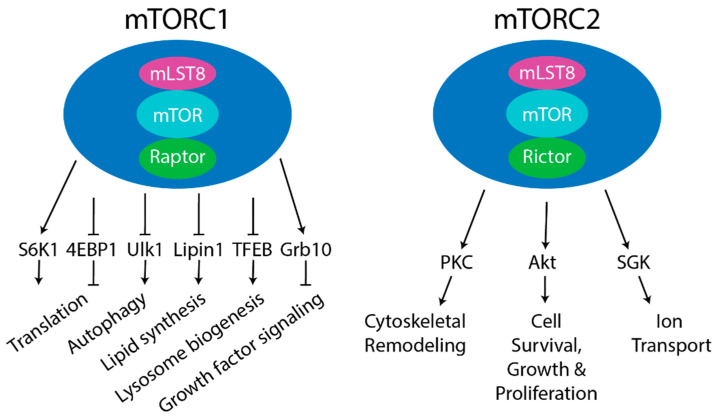
Figure 1.
Components of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2. Left- Core components of mTORC1 are mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) (kinase), Raptor (substrate recognizing component), and mLST8 (positive regulator). Other reported mTORC1 components are PRAS40 (negative regulator) and DEP-domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein (DEPTOR) (negative regulator). Five main downstream pathways are shown. The phosphorylation of S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) and 4EBP1 by mTORC1 regulates protein translation. The phosphorylation of ULK1 by mTORC1 regulates autophagy. mTORC1 also regulates lipid synthesis by phosphorylating S6K1 or Lipin1 to control SREBP, lysosome biogenesis by phosphorylating TFEB, and growth factor signaling by phosphorylating Grb10. Right- Core components of mTORC2 are mTOR (kinase), Rictor (substrate recognizing component), and mLST8 (positive regulator). Other complex components include mSin1 (positive regulator), Protor1/2 (positive regulator), and DEPTOR (negative regulator). mTORC2 regulated processes include cytoskeletal remodeling by phosphorylating PKC; cell survival, growth, and proliferation by phosphorylating Akt; and ion transport by phosphorylating SGK.