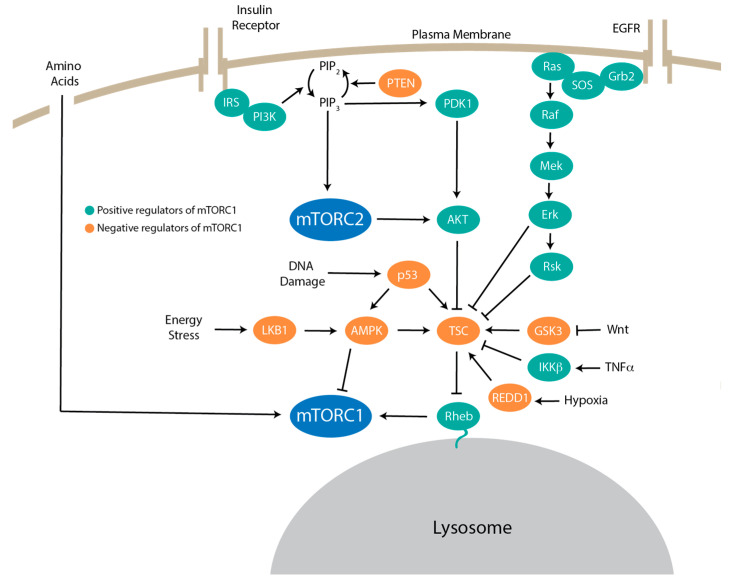
Figure 2.
The mTOR upstream signaling network. Upstream regulators of mTOR signaling. Positive regulators of mTORC1 are shown in turquoise and negative regulators are shown in orange. Growth factors activate PI3K though the binding of IRS proteins. PI3K then phosphorylates PIP2 to PIP3 which then activates PDK1/2. Akt, containing a specific PIP2 and PIP3 PH domain, localizes to the plasma membrane and then subsequently activates through PDK1 phosphorylation. Akt promotes mTORC1 activity through the phosphorylation of TSC, subsequently activating Rheb. mTORC2 also phosphorylates Akt. The Ras-Raf-Mek-Erk signaling cascade leads to the inhibition of TSC through Erk or Rsk. mTORC1 activity is also controlled by Wnt signaling, TNFα through IKKβ, hypoxia through REDD1, and DNA damage through p53. Energy stress activates negative regulators such as LKB1 and AMPK to inhibit mTORC1. Rac-α Ser/Thr-protein kinase (Akt also known as PKB); AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK); epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); extracellular signal-related kinase (Erk); GTPase activating protein (GAP); growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (Grb2); glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3); IκB kinase β (IKKβ); insulin receptor substrate (IRS); liver kinase B1 (LKB1); mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK); protein 53 (p53); pleckstrin homology (PH); phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1/2 (PDK1/2); phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K); phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2); phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3); phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN); rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (Raf); rat sarcoma (Ras); DNA damage response 1 (REDD1); Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb); p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (Rsk); son of sevenless homolog (SOS); tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα); tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC); wingless-type (Wnt).