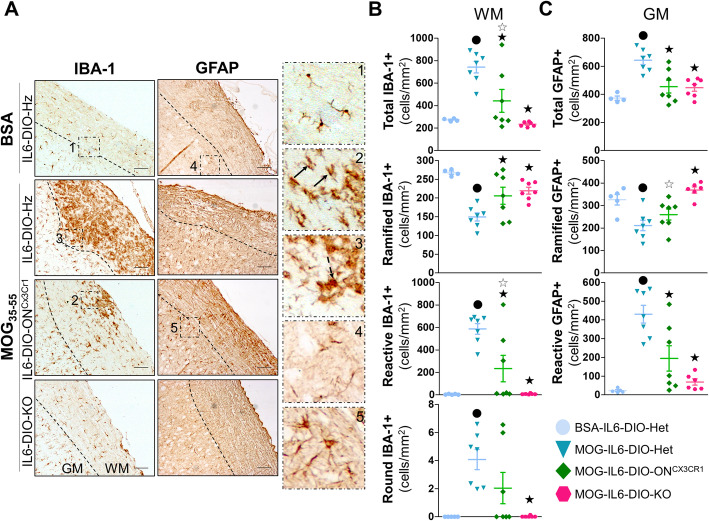
Fig. 8.
Microglial IL-6 plays a minor role in the regulation of microgliosis and astrogliosis. a Representative images of IBA-1 (left) and GFAP (middle) immunostaining of BSA-immunized IL6-DIO-Het and MOG35-55-immunized IL6-DIO-Het, IL6-DIO-ONCx3cr1 and IL6-DIO-KO mice. High magnification (right) of (a) showing the different morphologies of IBA-1+ and GFAP+ cells: (1) ramified, resting IBA-1+ cells; (2) reactive IBA-1+ cells, with shorter and thicker cell processes (black arrows); (3) round IBA-1+ cells (dashed black arrow); (4) Ramified, resting GFAP+ cells; (5) reactive, hypertrophic GFAP+ cells. The contrast of the representative images was enhanced. The discontinuous line delimits white matter (WM) from gray matter (GM). Scale bar: 100 μm. b The total number of IBA-1+ cells and the number of IBA-1+ cells showing a resting phenotype (ramified), partially activated (reactive), and fully activated (round) counted in the white matter of the spinal cord from BSA-immunized WT and MOG35-55-immunized IL6-DIO-Het, IL6-DIO-ONCx3cr1, and IL6-DIO-KO mice. c The total number of GFAP+ cells and the number of GFAP+ cells showing a resting phenotype (ramified) and activated (reactive) counted in the gray matter of the spinal cord from BSA-immunized WT and MOG35-55-immunized IL6-DIO-Het, IL6-DIO-ONCx3cr1, and IL6-DIO-KO mice. All results were relativized per total area and are represented as mean ± SEM; ●p ≤ 0.05 vs. BSA-IL6-DIO-Het mice; ★p ≤ 0.05 vs. IL6-DIO-Het mice. ☆p ≤ 0.05 vs. IL6-DIO-KO mice