FIG 7.
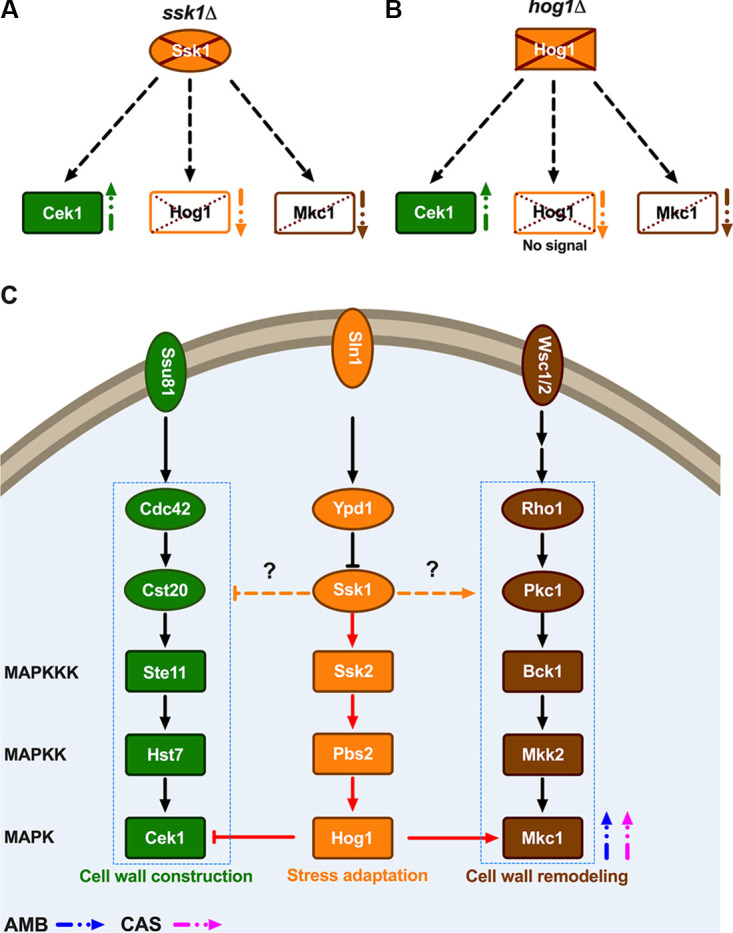
Model for MAPK signaling cross talk in response to antifungal drugs in C. auris. Linear MAP kinase pathways (MAPKKK→MAPKK→MAPK) are represented in rectangles; upstream components are in ovals. Cek1 (green)-, Hog1 (orange)-, and Mkc1 (brown)-containing MAPK pathways are color coded. Open rectangles indicate either absence or reduced phosphorylation. (A) Lack of Ssk1 protein increases p-Cek1 (upward green arrow), reduction or absence of p-Hog1 (downward orange arrow), and partial reduction of p-Mkc1 (downward brown arrow). (B) Absence of HOG1 increases p-Cek1 (upward green arrow) but reduces p-Mkc1 (downward brown arrow). (C) MAPK signaling pathways such as Cek1, Hog1, and Mkc1 are illustrated. Modulation of signaling is indicated with either stimulatory arrows (→) or inhibitory arrows (⊣). Amphotericin B (AMB) and caspofungin (CAS) treatment triggers Mkc1 phosphorylation (blue and pink arrows, respectively). The Ssk1-driven pathway including Hog1 cross talk with Cek1 and Mkc1 is shown in red arrows. Activating or inhibitory roles of Ssk1 may involve direct or indirect interactions with Ste11 or Cek1 (p-Cek1) or with Bck1 (p-Mkc1) (orange dashed arrows with question marks).
