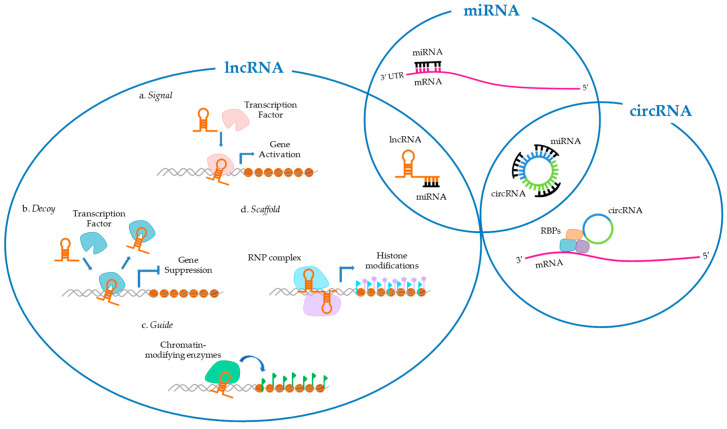
Figure 1.
Overview of the interactions and functions of ncRNAs in CSCC. ncRNAs are involved in several fundamental cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasiveness, and angiogenesis through chromatin remodelling, transcription, post-transcriptional modifications, and signal transduction. Specific activities of ncRNAs are limited in separated circles, while common involvements are reported in the overlapping circles. miRNAs can target mRNAs on the 3′ UTR site by inhibiting gene expression or circRNAs and lncRNAs by regulating their stability. In turn, circRNAs can directly regulate the gene transcription of mRNAs by binding and sequestering RNA-binding proteins (RBP) with the formation of the RNA-protein complex (RPC). In addition, both circRNAs (CDR1as, circ_0070934 [42]) and lncRNAs (HOTAIR [43],LINC00319 [46], LINC00963 [47]) can sequester miRNAs by acting as “miRNA sponges” in order to regulate their availability. lncRNAs are classified into four categories according to their functions: (a) as signals, helping genes transcription; (b) as decoys, binding and removing transcription factors from chromatin in order to suppress gene expression; (c) as guides, acting, either in cis or trans, on target genes and promoting their activation or repression through the recruitment of chromatin-modifying enzymes; (d) as scaffolds, forming a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex that affects histones modifications (MALAT [38]).