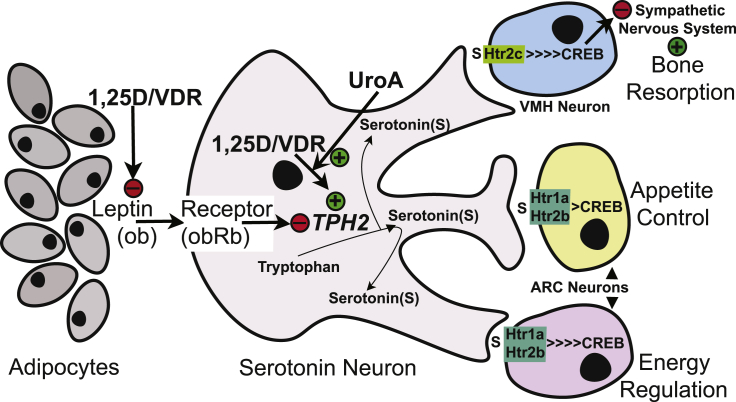
Fig. 6.
A model for the actions of 1,25D/VDR and its modulation by UroA on the serotonin-dependent neuronal relay that mediates leptin regulation of bone mass, appetite and energy expenditure. Leptin normally inhibits synthesis and release of brain-derived serotonin, favoring bone mass accrual, appetite, and energy metabolism. 1,25D represses adipocyte leptin and induces TPH2 to potentiate serotonin relay signaling via serotonergic nerve transmission at synapses in the cerebral cortex. Serotonin action is spurred by 1,25D and amplified by UroA at both presynaptic and postsynaptic sites through Type 1A and 2A serotonin receptors, respectively. VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus; ARC, arcuate nucleus.