Figure-2.
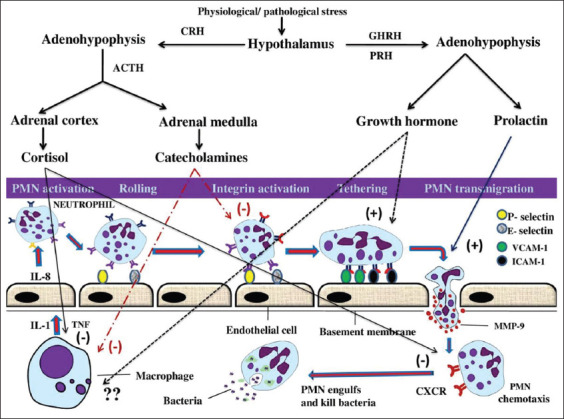
Stress modulation of the hormonal profile by the central nervous system. On experiencing an adverse stimulus (stressor), the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis and the sympathetic nervous system are activated resulting in the release of glucocorticoids and catecholamines, which can modulate and suppress various receptors and adhesion molecules involved in the activity of phagocytic cells. Furthermore, the pituitary hormones (prolactin and growth hormone) are also released which, however, enhance phagocytic cells activity. GHRH: Growth hormone-releasing hormone; PRH: Prolactin-releasing hormone; CRH: Corticotropin-releasing hormone; ACTH: Adrenocorticotropic hormone. Negative (−) sign indicates an inhibitory effect, while positive (+) sign indicates a stimulatory effect. (Source: Mohanned Naif Alhussien and Ajay Kumar Dang).
