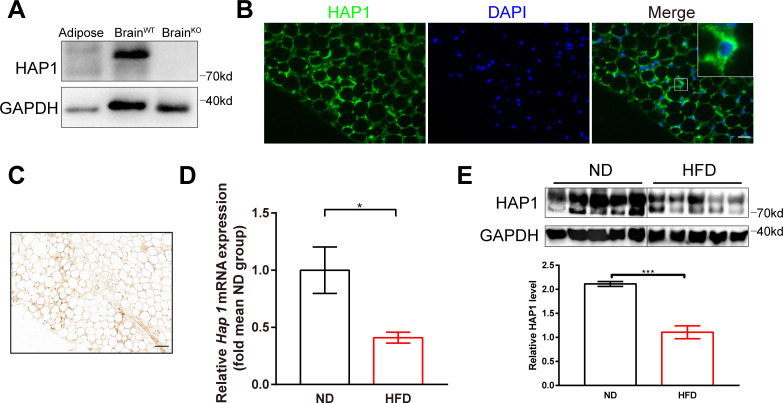
Figure 1.
Decreased expression of huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1) in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced diabetic mice. (A) Mouse adipose and brain tissues were harvested for detection of HAP1 by western blotting. Sample from wild-type (WT) brain was used as a positive control, and sample from Hap1-/- brain was used as a negative control. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of adipose tissue for HAP1 (green). Scale bar, 25 µm. (C) Immunohistochemistry staining of adipose tissue for HAP1. Scale bar, 50 µm. (D and E) Adipose tissues were harvested from both HFD and normal diet (ND)-fed mice at 25 weeks. (D) Hap1 mRNA quantification with quantitative PCR. β-actin was used as the internal reference (n=3 animal per group). (E) HAP1 protein assessed by western blotting. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a loading control (n=5 per group). Data are presented as mean±SEM. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 (unpaired two-tailed t tests). DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.