Figure 3.
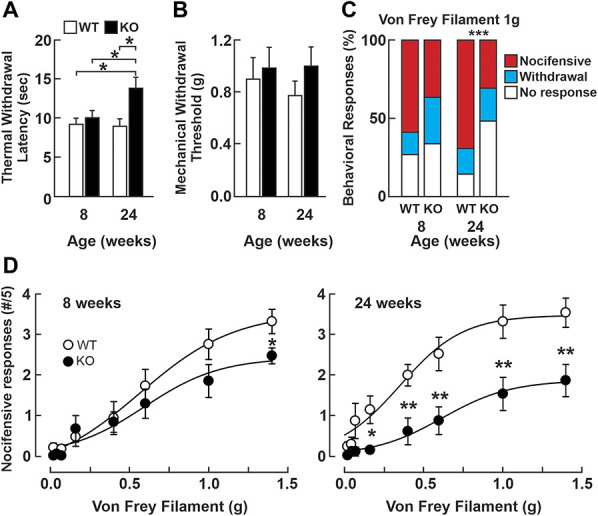
Mice lacking the NHE6 exchanger have decreased responses to noxious thermal and mechanical stimuli. (A) Mean (±SEM) paw withdrawal latency measured in the Hargreaves test for heat sensitivity in NHE6 WT (n = 10) and KO (n = 5) mice. *P < 0.05, paired t test. (B) Mean (±SEM) mechanical withdrawal thresholds measured with von Frey filaments. No significant differences are observed between the genotypes or over time. One-way ANOVA, P = 0.619 (8-week-old NHE6 WT (n = 10) and KO (n = 8); 24-week-old NHE6 WT (n = 10) and KO (n = 12). (C) Distribution (%) of behavioral responses to von Frey filament stimuli. The distributions of the behavioral responses to a 1.0 g mechanical stimulus are not significantly different between in 8-week-old WT (n = 10) and KO (n = 8) mice. Fisher exact test, P = 0.064. When assessed in 24-week-old mice, there is a significant change in the distribution of the responses of NHE6 KO mice, with an increase in the “no response” group (14.5% in WT, n = 10 vs 49.3% in KO, n = 12), and a decrease in the “nocifensive response” group (69.1% in WT vs 30.7% in KO), contingency table P < 0.001. (D) Nocifensive responses to von Frey filaments in 8-week-old NHE6 WT (n = 10) and KO (n = 8) mice (left panel) and 24-week-old NHE6 WT (n = 10) and KO (n = 12) mice (right panel). Student t-test; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. ANOVA, analysis of variance; KO, knockout; WT, wild-type.
