Fig. 1.
Dynamic changes in the immune system during sepsis progression.
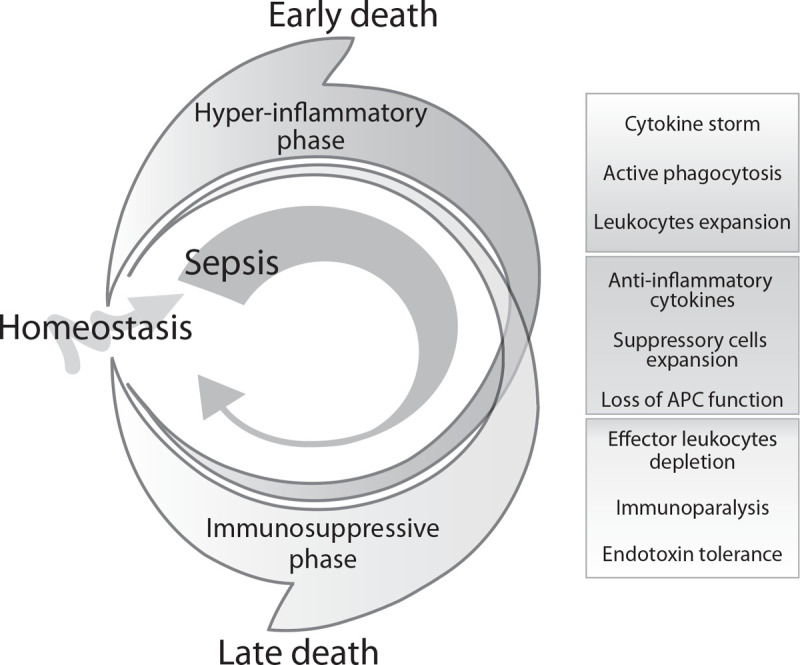
During initial phase of sepsis, the hyperinflammatory phase develops and is associated with cytokine storm, active removing of pathogens by phagocytosis and expansion of different leukocyte types. Too excessive hyperinflammatory phase can lead to early death of septic patients. During progression of sepsis, production of anti-inflammatory cytokines is progressively augmented leading to disbalance of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines levels. This fact also contributes to the expansion of suppressory cells and loss of antigen presenting function. Subsequently, when the immunosuppressive phase completely prevails, the depletion of effectory cells contributes to immunoparalysis of immune system. The disproportionate levels during immunosuppressive phase can cause late death of patients during progression of sepsis. The immunoparalysis as well as endotoxin tolerance can persis also when the homeostasis is restored.
