Fig. 4. Cryo-EM structure of NusA-NusG-TTC-B.
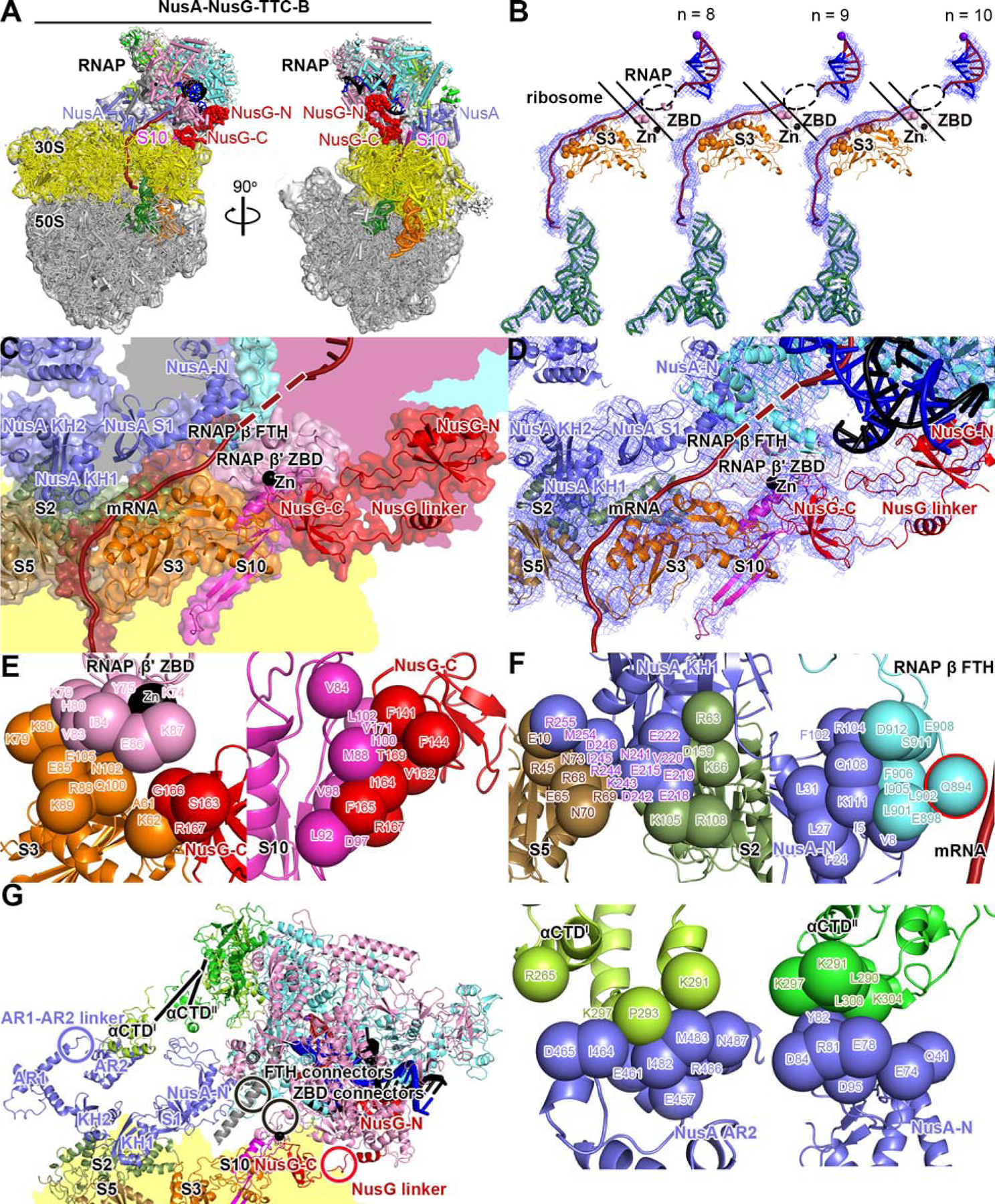
(A) Structure of NusA-NusG-TTC-B (NusA-NusG-TTC-B2; 3.5 Å; n = 9; Table S1). NusA, light blue. Views and other colors as in Figs. 2A and 3A.
(B) Accommodation of mRNA spacer lengths of 8, 9, and 10 codons in NusA-NusG-TTC-B. Views and colors as in Fig 3B.
(C) RNAP-ribosome interface, NusG bridging, and NusA binding in NusA-NusG-TTC-B (n = 9; identical interface for n = 8, 9, or 10). RNAP β’ zinc binding domain, (ZBD, pink; Zn2+ ion as black sphere) interacts with ribosomal protein S3 (orange) and mRNA (brick red). NusG (red) bridges RNAP and ribosome, with NusG-N interacting with RNAP and NusG-C interacting with ribosomal protein S10 (magenta). NusA (light blue) KH1 domain interacts with ribosomal proteins S5 and S2 (brown and forest green). Portions of RNAP β’, β, ω, and ribosome 30S not involved in interactions are shaded pink, cyan, gray, and yellow, respectively.
(D) As C, showing cryo-EM density as blue mesh.
(E) RNAP-ribosome interactions involving RNAP β’ ZBD and S3 (subpanel 1) and NusG-ribosome interactions involving NusG-C and S10 (subpanel 2).
(F) NusA-ribosome interactions involving NusA KH1 and S5 and S2 (subpanel 1) and NusA-RNAP interactions involving NusA-N and RNAP β FTH (subpanel 2; β FTH residue that interacts with mRNA, cyan sphere with red outline; mRNA, brick-red), NusA AR2 and RNAP αCTDI (subpanel 3), and NusA-N and RNAP αCTDII (subpanel 4).
(G) Points of flexibility in NusA-NusG-TTC-B (NusA “coupling pantograph”): flexible linkage in NusA structure (AR1-AR2 linker; light blue circle), three flexible linkages between NusA and RNAP (αCTDI linker, αCTDII linker, and β FTH connectors; black lines and black circle), flexible linkage between RNAP and ribosome (β’ ZBD connectors; black circle), and flexible NusG bridging of RNAP and ribosome (NusG linker; red circle).
