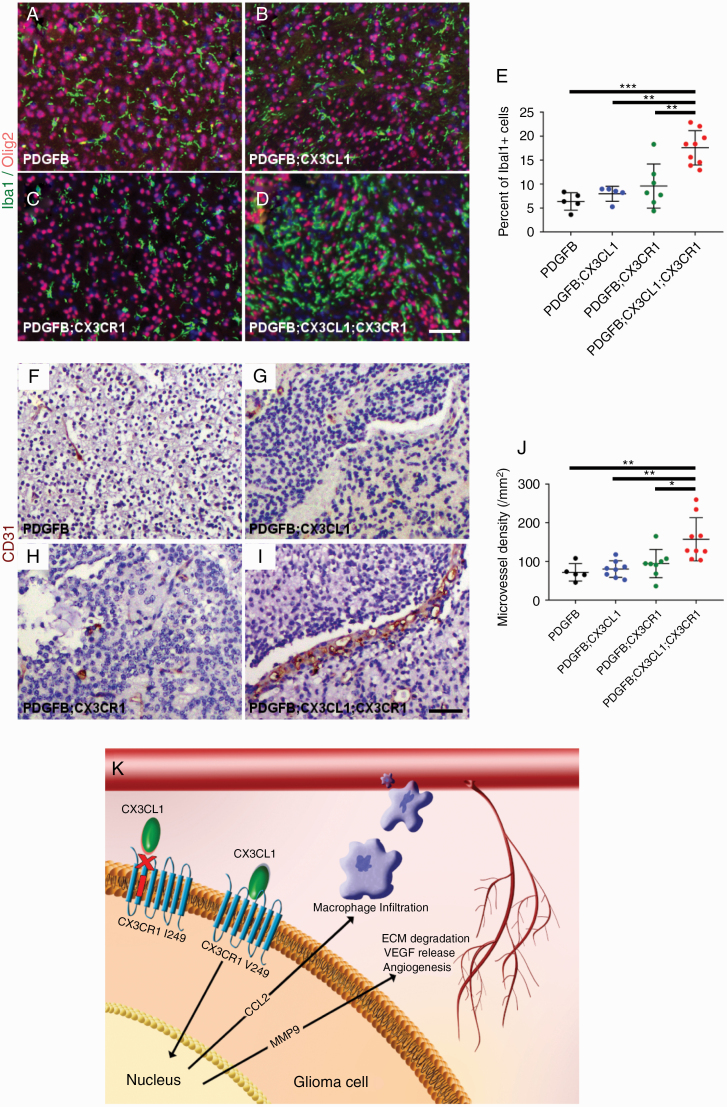
Fig. 5.
Histologic sections of murine HGGs from PDGFB (n = 5; A), PDGFB;CX3CL1 (n = 5; B), PDGFB;CX3CR1 (n = 7; C), and PDGFB;CX3CL1;CX3CR1 groups (n = 9; D) were immunostained with antibodies against microglia/macrophage marker Iba1 (green, A–D) and oligodendroglial lineage and tumor marker Olig2 (red, A–D), followed by counterstaining with DAPI (blue, A–D). Tumors from PDGFB;CX3CL1;CX3CR1 group exhibited significantly increased accumulation of microglia/macrophages, compared with tumors from all other groups (E). Histological sections of murine HGGs from PDGFB (n = 5; F), PDGFB;CX3CL1 (n = 8; G), PDGFB;CX3CR1 (n = 8; H), and PDGFB;CX3CL1;CX3CR1 groups (n = 9; I) were immunostained with antibody against endothelial marker CD31 (brown, F–I), followed by counterstaining with hematoxylin (blue, F–I). Tumors from PDGFB;CX3CL1;CX3CR1 group exhibited significantly increased density of CD31-positive microvessels, compared with tumors from all other groups (J). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test. Scale bar, 50 μm. (K) Working model. In gliomas, CX3CR1 signaling promotes CCL2-dependent TAM infiltration and MMP9-driven angiogenesis, which is abrogated by the I249 variant allele. ECM, extracellular matrix; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.