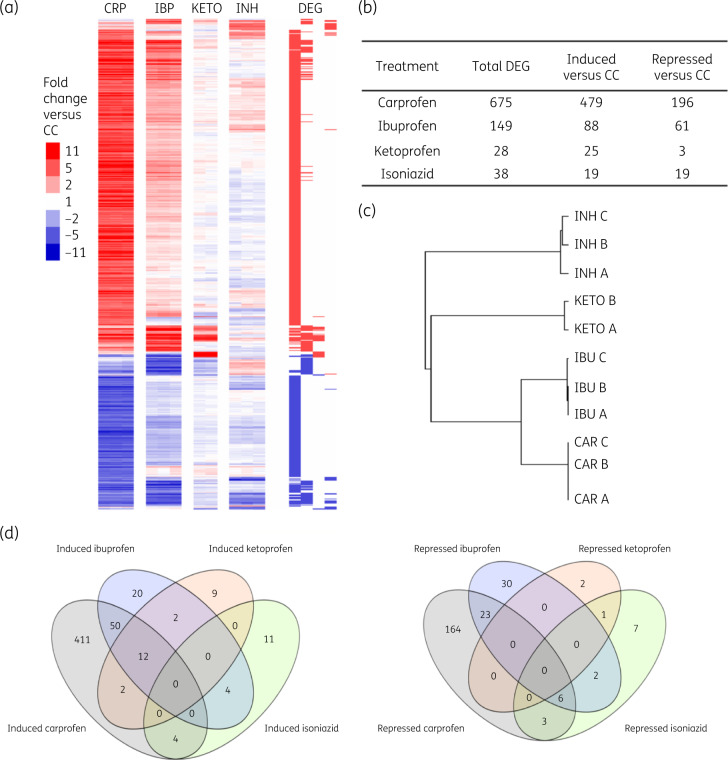
Figure 2.
Transcriptional response of M. tuberculosis H37Rv to 4 h carprofen exposure (10× MIC, 400 mg/L). (a) Heatmap showing the NSAID drug signatures. Each column represents a drug treatment biological replicate and each row represents the expression profile of a gene relative to carrier control. Red colouring indicates induction and blue indicates repression. CRP, carprofen; IBP, ibuprofen; KETO, ketoprofen; INH, isoniazid; CC, carrier control. The genes identified as significantly differentially expressed in each drug comparison are marked as DEG. (b) Total number of genes that were significantly up- and down-regulated by drug exposure. (c) Hierarchical clustering of M. tuberculosis responses to drug exposure, showing similarity between replicate treatments (carprofen represented as CAR here). (d) The number of genes significantly modified by each drug exposure in comparison with carrier control. Overlap of genes induced or repressed by exposure to NSAIDs, showing minimal response to ketoprofen and discrete isoniazid signature.