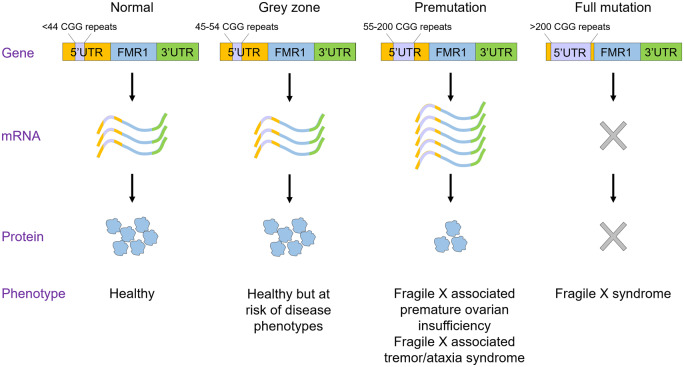
Figure 1.
CGG repeat length is polymorphic. Normal individuals have fewer than 44 CGG repeats (mean 29) and CGG repeat lengths between 45 and 54 are termed grey zone, as they are at risk of developing disease phenotypes due to CGG repeat instability. Individuals with a premutation have between 55 and 200 CGG repeats, elevated FMR1 mRNA levels and reduced FMRP protein levels, and the premutation causes the conditions fragile X-associated premature ovarian insufficiency and fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Individuals with more than 200 CGG repeats have a full mutation, where the FMR1 gene is transcriptionally silenced, leading to an absence of FMR1 mRNA and FMRP protein. The full mutation causes fragile X syndrome. Figure adapted from Hagerman and Hagerman (2002).