Figure 2.
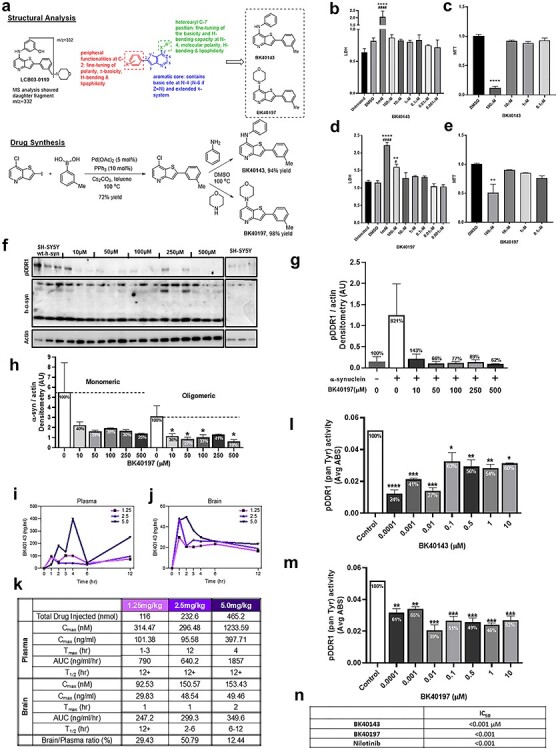
Synthesis, effects and potency of novel DDR1 inhibitors. (A) Schematic of structural analysis of LCB-03-0110, structure activity relationship and synthesis of BK40143 and BK40197. Cell viability of BK40143 and BK40197 via (B) LDH and (C) MTT of DMSO, 1 mM, 100, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01 and 0.001 μM BK40143-treated and untreated B35 rat neuroblastoma cells. (D) LDH and (E) MTT cell viability assays of DMSO, 1 mM, 100, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01 and 0.001 μM BK40197-treated and untreated B35 rat neuroblastoma cells. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 to DMSO group, ####P < 0.0001 to untreated group; normal one-way ANOVA; n = 3 per treatment group. (F) Western blot of pDDR1, α-synuclein and actin SHSY-5Y stably transfected with human α-synuclein treated with 1, 50, 100, 250 and 500 μM of BK40197 for 5 h and untreated. (H) Quantification of monomeric and oligomeric human α-synuclein and (G) pDDR1 with percentage change from untreated group, each normalized to actin. *P < 0.05; normal one-way ANOVA; n = 3 per treatment group. (I) Plasma concentration (nM) and (J) brain concentration (nM) of 1.25, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg doses of BK40143 at 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12 h after I.P injection in C57BL/6 mice determined by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. (K) Table of pharmacokinetic properties including Cmax (nM) and (ng/ml), Tmax, area under the curve (AUC) (ng/ml/h), t1/2 (h) and the ratio of brain to plasma concentrations on the basis of 1.25, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg doses of BK40143. ELISA for human pDDR1 (mean absorbance (ABS)) from human wild-type α-synuclein stably transfected SHSY-5Y cells treated with 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10 μM of (L) BK40143 and (M) BK40197 for 5 h and untreated groups. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001; normal one-way ANOVA; n = 3 per group. (N) Table of IC50 for BK40143, BK40197, nilotinib for pDDR1.
