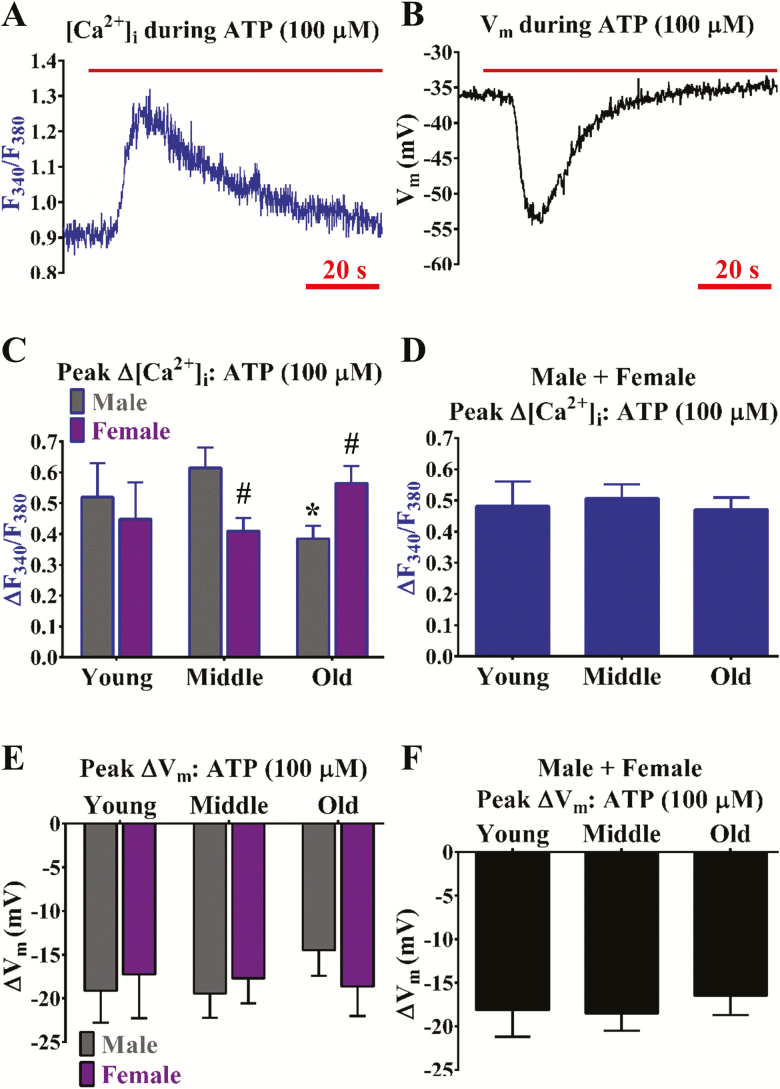
Figure 1.
Purinergic receptor function for increasing [Ca2+]i is enhanced in females and declined in males during old age. Representative simultaneous recordings of (A) Fura-2 for [Ca2+]i and (B) a sharp electrode for Vm before and during ATP (100 µmol/L; purinergic receptor agonist and indirect SKCa/IKCa channel activator) in an isolated endothelial tube of a young male. (C) Summary data for ΔF340/F380 during ATP as a function of age (Young, Middle, Old) and sex (Male, Female). (D) As shown in (C) as a function of age only (sexes combined). (E, F) As shown in (C) and (D), respectively, for ∆Vm. n = number of cerebral endothelial tubes (Young, Middle, and Old: 7, 9, and 12 Males and 8, 10, and 11 Females; combined for age only: 15, 19, & 23). *p < .05, Old versus Middle; #p < .05, Female versus Male for same age group. Note that ∆[Ca2+]i and ∆Vm responses to ATP decreased upon old age for males but not females. With data from respective sexes combined, such differences with age are no longer apparent.