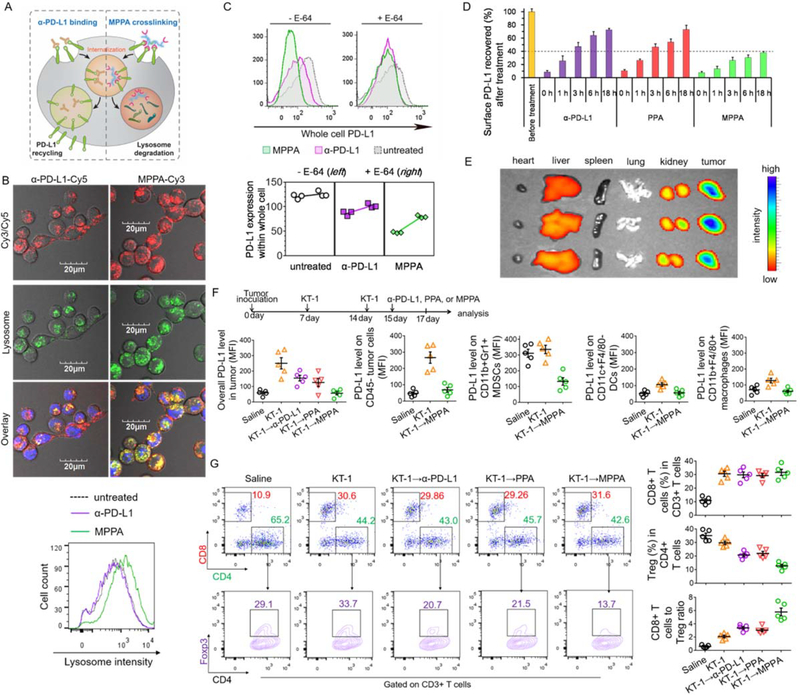
Figure 4. Crosslinking surface PD-L1 by MPPA directs PD-L1 to lysosomal degradation.
(A) Schematic illustration of inhibiting PD-L1 recycling by MPPA crosslinking. (B) Lysosome colocalization of α-PD-L1-Cy5 or Cy3-labeled MPPA (P-(PPA)14-Cy3) and lysosome intensity evaluation after 3 h treatment at 37 °C. Blue: nuclei; Red: Cy3/Cy5; Green: lysosomes. (C) Whole cell PD-L1 expression with or without lysosome hydrolysis inhibition by E-64. 4T1 cells were treated with α-PD-L1, PPA, or MPPA for 3 h in the absence (−) or presence (+) of E-64 cysteine protease inhibitor. Afterward, cells were further incubated in cell culture medium for another 24 h, prior to PD-L1 quantification. (D) Time-dependent recovery of surface PD-L1 after treatments with α-PD-L1, PPA, or MPPA. 4T1 cell surface was precoated with saturating concentration of antibody, peptide, or conjugates at 4 °C for 2 h. Then cells were washed and incubated with fresh cell culture medium at 37 °C. At selected time points (0, 1, 3, 6 h), surface accessible PD-L1 receptors were stained with fluorophore-labeled anti-PD-L1 antibody and measured by flow cytometry. (E) Biodistribution of MPPA-Cy5 in major organs in mice after 24 h post iv injection (n=3). (F) PD-L1 level on CD45- tumor cell, CD11b+GR1+ MDSCs, CD11c+F4/80- DCs, and CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages, and (G) analysis of CD8+ T cells and CD4+Foxp3+ Tregs in tumors after KT-1 and MPPA combination treatment as indicated by arrows in (E). n=3 in (C) and (D), and n=5 in (E) and (F).