Figure 4. Establishing local regulation of GLUR1 by NMD in dendrites.
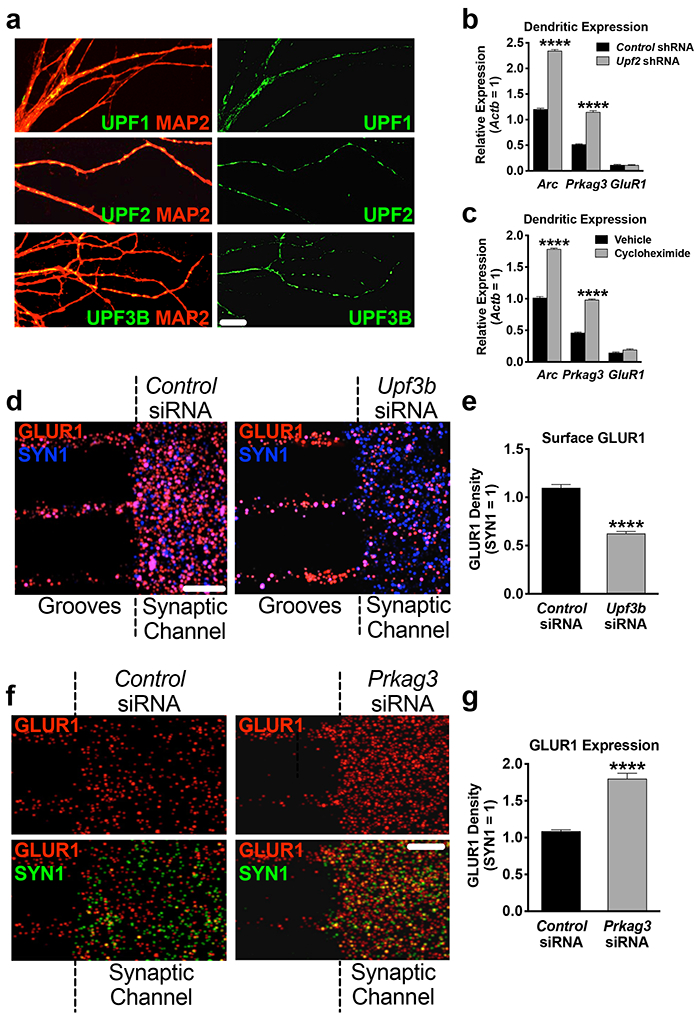
a, The NMD machinery is localized to dendrites.
UPF1, UPF2 and UPF3B immunostainings in hippocampal dendrites at DIV7.
b, Arc and Prkag3 mRNAs are increased in UPF2-deficient dendrites.
Synaptic material was harvested from tripartite chambers containing postsynaptic neurons infected with either control- or Upf2-shRNA virus (n=3) and qRT-PCR for Arc and Prkag3 mRNAs was performed.
c, Arc and Prkag3 mRNAs are subjected to translation-dependent degradation in dendrites. Selective treatment of synaptic channels with the translation inhibitor CHX (10 μM) at DIV21 for 3 hr and qRT-PCR for Arc and Prkag3 mRNAs (n=3).
d, NMD locally regulates surface expression of GLUR1 in dendrites.
Repetitive treatment of synaptic channels with non-overlapping Upf3b-siRNAs (10 nM) for 7 days led to complete loss of UPF3B protein (Figure S9d) and a >40% decrease in surface GLUR1 compared to control cultures (10 neurons, 10 dendrites per group).
e, Locally synthesized PRKAG3 negatively regulates GLUR1 levels in dendrites. Quantifications of total GLUR1 levels following non-overlapping Prkag3 siRNA treatment of synaptic channels for 7d (n=3 per control-siRNA [6 neurons, 9 dendrites] and per Prkag3-siRNA [8 neurons, 9 dendrites]).
Data are represented as mean ± SEM; ****p < 0.0001. Scale bar: 30 μm.
