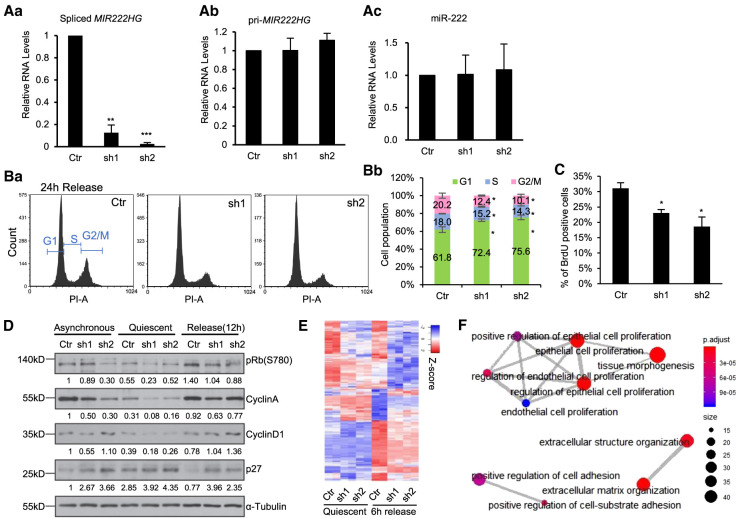
FIGURE 5.
Spliced mature MIR222HG facilitates cell cycle reentry post quiescence in a micro-RNA independent manner. (A) RT-qPCR to quantify the levels of (a) spliced MIR222HG, (b) pri-MIR222HG, and (c) mature miR-222 (TaqMan assay), in control and MIR222HG shRNA treated WI-38 cells. (B) (a) PI-flow cytometry analyses in control and MIR222HG-depleted WI-38 cells at 24 h postserum stimulation. (b) Percentage of cells at a specific cell cycle stage in control and MIR222HG-depleted cells. Data obtained from biological triplicates. Quantification is performed using FCS Express. (C) Percentage of BrdU-incorporated cells in control and MIR222HG-depleted WI-38s at 24 h postserum stimulation. (D) Immunoblot to detect the levels of several cell cycle marker proteins in control and MIR222HG-depleted asynchronous, quiescent, and serum-stimulated (12 h) WI-38 cells. α-Tubulin is used as loading control. Quantification was performed with Image J. Relative protein levels were calculated by normalizing with GAPDH, followed by comparing to the asynchronous control sample. Values are labeled on the bottom of each blot. (E) Heatmaps showing the relative expression of 398 differentially expressed genes in control and MIR222HG-depleted cells during quiescence and 6-h serum stimulation, obtained by RNA-seq. Biological duplicates are represented. Genes (rows of heatmap) are hierarchically clustered using average-linkage clustering method. Detailed DEG information is available in Supplemental Table S6. (F) Gene ontology (GO) analyses showing the top enriched biological processes that show changes in MIR222HG-depleted cells. (*) P ≤ 0.05, (**) P ≤ 0.01, (***) P ≤ 0.001, (****) P ≤ 0.0001 by two-tailed Student's t-test, n = 3 for all figures. Error bars represent standard deviation.