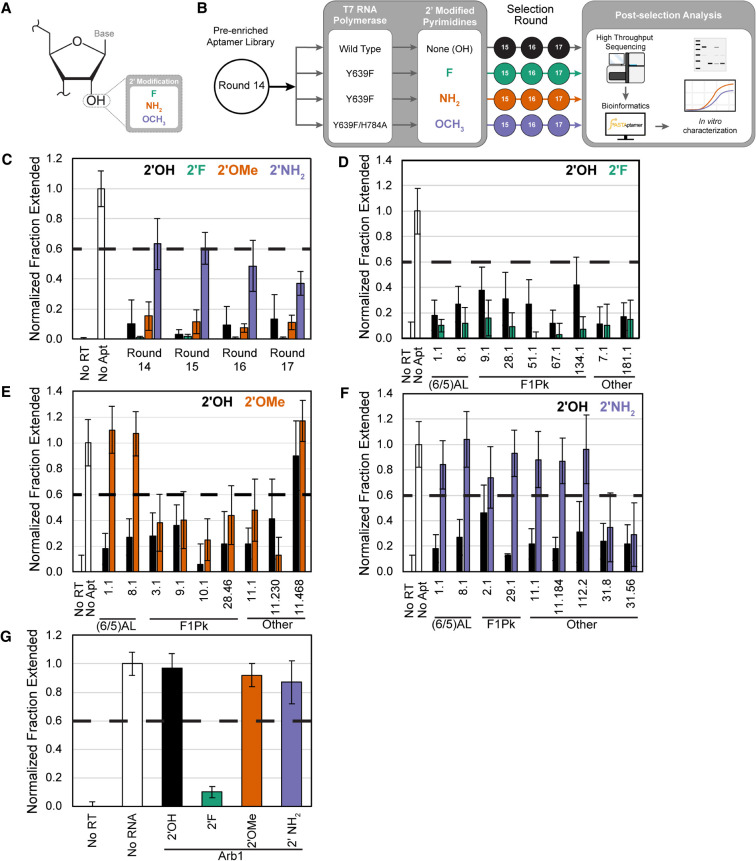
FIGURE 1.
Effect of 2′-pyrimdine modifications on RT inhibition by candidate aptamers. (A) Structure of ribose in RNA highlighting the 2′ position and modifications tested in this study. (B) Schematic of the reselection strategy. A preenriched aptamer library that had previously undergone 14 rounds of selection for affinity to HIV-1 RT was transcribed with either 2′-OH, 2′-F, 2′-OMe, or 2′-NH2 pyrimidines and reselected for three additional rounds, with each trajectory performed in duplicate. (C) Quantification of primer extension assays showing fraction of primer converted into full-length product in control reactions in the absence of RT (No RT) or aptamer (No Apt) and in reactions containing selected aptamer libraries from the 2′-OH (black), 2′-F (green), 2′-OMe (orange), or 2′-NH2 (purple) trajectory after each reselection round. (D–F) Quantification of primer extension assays showing fraction of primer converted into full-length product in control reactions in the absence of RT (No RT) or aptamer (No Apt) or in reactions containing aptamers transcribed with either 2′-OH or (D) 2′-F, (E) 2′-OMe, or (F) 2′-NH2 pyrimidines. Aptamers are grouped together by structural class: (6/5) asymmetric loop family [(6/5)AL] or family 1 pseudoknot (F1Pk). Aptamers that did not contain the consensus sequence features of any of the characterized structural motifs were grouped as Other. (G) Evaluation of primer extension assays in the presence of 2′-modified Arb1. Plotted values and vertical error bars represent the means and standard deviations of fraction primer extended to full-length product normalized to the no aptamer (or no RNA) control (set to 1) and to the no RT control (set to 0) of four independent replicates (n = 4). RNAs are considered inhibitory if the normalized fraction extended value is below 0.6, which is marked by a dashed horizontal line.