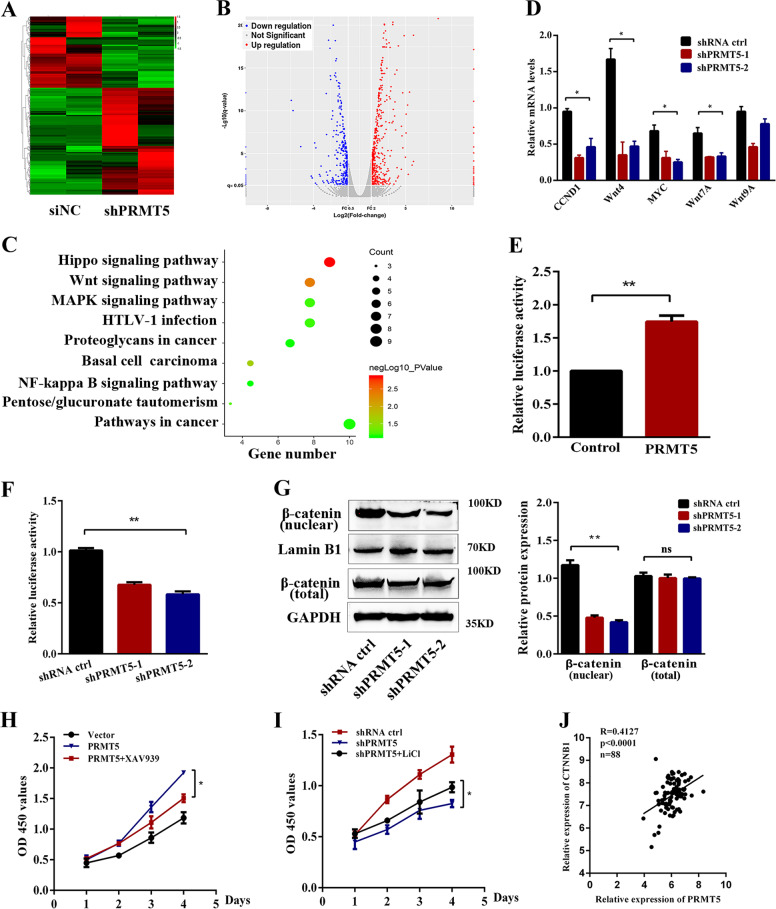
Fig. 4. PRMT5 regulates the proliferation of laryngeal carcinoma via the Wnt signaling pathway.
a Heatmap representing gene expression changed between shPRMT5 and shRNA ctrl cells. Red and blue indicate high and low mRNA expression, respectively. b Volcano plot representing gene expression differences in PRMT5-slienced Tu686 cells. Each gene is represented by a dot with the red or blue dots indicating the differentially expressed transcripts that are statistically significant. c KEGG enrichment analysis showed the distribution of terms exhibiting statistically significant differences. d The relative mRNA levels of the indicated genes were normalized to the GAPDH level in the Tu686 cells stably transfected with control or shPRMT5 as determined by qRT-PCR. The results are expressed as the mean + SD of three independent experiments. e Luciferase reporter assay for its activity of overexpressing PRMT5 increased Topflash reporter activities in Tu212 cells. f Knockdown of PRMT5 impaired Topflash reporter activities in Tu686 cells. g The expression of β-catenin (nuclear and total) was determined by western blotting in PRMT5-knockdown Tu686 cells. h, i Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor XAV939 or activator LiCl dramatically suppressed or restarted cell proliferation of PRMT5 mediated, respectively. j Pearson correlation analysis was performed between PRMT5 and β-catenin expression in our first cohort of samples. Data are the mean ± SD of three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.